Neutralization of osteopontin inhibits obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance
- PMID: 20107108
- PMCID: PMC2844841
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-0404
Neutralization of osteopontin inhibits obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance
Abstract
Objective: Obesity is associated with a state of chronic low-grade inflammation mediated by immune cells that are primarily located to adipose tissue and liver. The chronic inflammatory response appears to underlie obesity-induced metabolic deterioration including insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Osteopontin (OPN) is an inflammatory cytokine, the expression of which is strongly upregulated in adipose tissue and liver upon obesity. Here, we studied OPN effects in obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance by targeting OPN action in vivo.
Research design and methods: C57BL/6J mice were fed a high-fat diet to induce obesity and were then intravenously treated with an OPN-neutralizing or control antibody. Insulin sensitivity and inflammatory alterations in adipose tissue and liver were assessed.
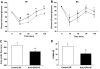
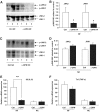
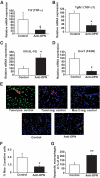
Results: Interference with OPN action by a neutralizing antibody for 5 days significantly improved insulin sensitivity in diet-induced obese mice. Anti-OPN treatment attenuated liver and adipose tissue macrophage infiltration and inflammatory gene expression by increasing macrophage apoptosis and significantly reducing c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase activation. Moreover, we report OPN as a novel negative regulator for the activation of hepatic signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), which is essential for glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity. Consequently, OPN neutralization decreased expression of hepatic gluconeogenic markers, which are targets of STAT3-mediated downregulation.
Conclusions: These findings demonstrate that antibody-mediated neutralization of OPN action significantly reduces insulin resistance in obesity. OPN neutralization partially decreases obesity-associated inflammation in adipose tissue and liver and reverses signal transduction related to insulin resistance and glucose homeostasis. Hence, targeting OPN could provide a novel approach for the treatment of obesity-related metabolic disorders.
Figures




References
-
- Despres JP, Lemieux I: Abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature 2006; 444: 881– 887 - PubMed
-
- Bastard JP, Maachi M, Lagathu C, Kim MJ, Caron M, Vidal H, Capeau J, Feve B: Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Eur Cytokine Netw 2006; 17: 4– 12 - PubMed
-
- Shoelson SE, Herrero L, Naaz A: Obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Gastroenterology 2007; 132: 2169– 2180 - PubMed
-
- Hotamisligil GS: Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 2006; 444: 860– 867 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

