OSU-03012 enhances Ad.7-induced GBM cell killing via ER stress and autophagy and by decreasing expression of mitochondrial protective proteins
- PMID: 20107314
- PMCID: PMC2888700
- DOI: 10.4161/cbt.9.7.11116
OSU-03012 enhances Ad.7-induced GBM cell killing via ER stress and autophagy and by decreasing expression of mitochondrial protective proteins
Abstract
The present studies focused on determining whether the autophagy-inducing drug OSU-03012 (AR-12) could enhance the toxicity of recombinant adenoviral delivery of melanoma differentiation associated gene-7/interleukin-24 (mda-7/IL-24) in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cells. The toxicity of a recombinant adenovirus to express MDA-7/IL-24 (Ad.mda-7) was enhanced by OSU-03012 in a diverse panel of primary human GBM cells. The enhanced toxicity correlated with reduced ERK1/2 phosphorylation and expression of MCL-1 and BCL-XL, and was blocked by molecular activation of ERK1/2 and by inhibition of the intrinsic, but not the extrinsic, apoptosis pathway. Both OSU-03012 and expression of MDA-7/IL-24 increased phosphorylation of PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) that correlated with increased levels of autophagy and expression of dominant negative PERK blocked autophagy induction and tumor cell death. Knockdown of ATG5 or Beclin1 suppressed OSU-03012 enhanced MDA-7/IL-24-induced autophagy and blocked the lethal interaction between the two agents. Ad.mda-7-infected GBM cells secreted MDA-7/IL-24 into the growth media and this conditioned media induced expression of MDA-7/IL-24 in uninfected GBM cells. OSU-03012 interacted with conditioned media to kill GBM cells and knockdown of MDA-7/IL-24 in these cells suppressed tumor cell killing. Collectively, our data demonstrate that the induction of autophagy and mitochondrial dysfunction by a combinatorial treatment approach represents a potentially viable strategy to kill primary human GBM cells.
Figures
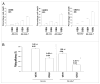




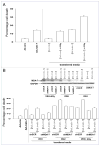

Comment in
-
The role of autophagy as a mechanism of cytotoxicity by the clinically used agent MDA-7/IL-24.Cancer Biol Ther. 2010 Apr 1;9(7):537-8. doi: 10.4161/cbt.9.7.11381. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20234182 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Robins HI, Chang S, Butowski N, Mehta M. Therapeutic advances for glioblastoma multiforme: current status and future prospects. Curr Oncol Rep. 2007;9:66–70. - PubMed
-
- Jiang H, Lin JJ, Su ZZ, Goldstein NI, Fisher PB. Subtraction hybridization identifies a novel melanoma differentiation associated gene, mda-7, modulated during human melanoma differentiation, growth and progression. Oncogene. 1995;11:2477–86. - PubMed
-
- Ekmekcioglu S, Ellerhorst J, Mhashilkar AM, Sahin AA, Read CM, Prieto VG, et al. Downregulated melanoma differentiation associated gene (mda-7) expression in human melanomas. Int J Cancer. 2001;94:54–9. - PubMed
-
- Ellerhorst JA, Prieto VG, Ekmekcioglu S. Loss of MDA-7 expression with progression of melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:1069–74. - PubMed
-
- Huang EY, Madireddi MT, Gopalkrishnan RV, Leszczyniecka M, Su Z, Lebedeva IV, et al. Genomic structure, chromosomal localization and expression profile of a novel melanoma differentiation associated (mda-7) gene with cancer specific growth suppressing and apoptosis inducing properties. Oncogene. 2001;20:7051–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA108520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-NS031492/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA134721/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA063753/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK52825/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA134721/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA097318/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA108325/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA141703/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA104177/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-CA104177/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS031492/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK052825/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA097318/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
