Critical role of Th17 responses in a murine model of Neisseria gonorrhoeae genital infection
- PMID: 20107432
- PMCID: PMC2857675
- DOI: 10.1038/mi.2009.139
Critical role of Th17 responses in a murine model of Neisseria gonorrhoeae genital infection
Abstract
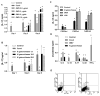
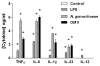
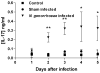
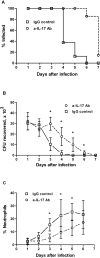
Host immune responses, including the characteristic influx of neutrophils, against Neisseria gonorrhoeae are poorly understood; adaptive immunity is minimal and non-protective. We hypothesize that N. gonorrhoeae selectively elicits Th17-dependent responses, which trigger innate defense mechanisms, including neutrophils and antimicrobial proteins, that it can resist. We found that N. gonorrhoeae induced the production of interleukin-17 (IL-17) in mouse T-cells and Th17-inducing cytokines in mouse and human APCs in vitro. IL-17 was induced in the iliac lymph nodes in vivo in a female mouse model of genital tract gonococcal infection. Antibody blockade of IL-17 or deletion of the major IL-17 receptor (IL-17R) in IL-17RA(KO) mice led to prolonged infection and diminished neutrophil influx. Genital tract tissue from IL-17RA(KO) mice showed reduced production of neutrophil-attractant chemokines in response to culture with N. gonorrhoeae. These results imply a crucial role for IL-17 and Th17 cells in the immune response to N. gonorrhoeae.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Diversion of the immune response to Neisseria gonorrhoeae from Th17 to Th1/Th2 by treatment with anti-transforming growth factor β antibody generates immunological memory and protective immunity.mBio. 2011 May 24;2(3):e00095-11. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00095-11. Print 2011. mBio. 2011. PMID: 21610119 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of host adaptive immune responses by Neisseria gonorrhoeae: role of interleukin 10 and type 1 regulatory T cells.Mucosal Immunol. 2014 Jan;7(1):165-76. doi: 10.1038/mi.2013.36. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Mucosal Immunol. 2014. PMID: 23757303 Free PMC article.
-
Female Mouse Model of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Infection.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1997:413-429. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9496-0_24. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31119637
-
Th17 cells and mucosal host defense.Semin Immunol. 2007 Dec;19(6):377-82. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2007.10.009. Epub 2007 Nov 28. Semin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 18054248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-17 and its expanding biological functions.Cell Mol Immunol. 2010 May;7(3):164-74. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2010.21. Epub 2010 Apr 12. Cell Mol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20383173 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial vaginosis-driven changes in cervicovaginal immunity that expand the immunological hypothesis for increased HIV susceptibility.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 14:2024.07.03.601916. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.03.601916. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39005354 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Immune Responses to Neisseria gonorrhoeae: Challenges and Opportunities With Respect to Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.J Infect Dis. 2021 Aug 16;224(12 Suppl 2):S96-S102. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa766. J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34396399 Free PMC article.
-
Innate and adaptive immunity at mucosal surfaces of the female reproductive tract: stratification and integration of immune protection against the transmission of sexually transmitted infections.J Reprod Immunol. 2011 Mar;88(2):185-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2011.01.005. Epub 2011 Feb 26. J Reprod Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21353708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-17-related signature genes linked to human necrotizing enterocolitis.BMC Res Notes. 2021 Mar 4;14(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s13104-021-05489-9. BMC Res Notes. 2021. PMID: 33663574 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-17A Contributes to the Control of Streptococcus pyogenes Colonization and Inflammation of the Female Genital Tract.Sci Rep. 2016 May 31;6:26836. doi: 10.1038/srep26836. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27241677 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harrington LE, et al. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1123–1132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

