Complete genome sequence of the multiresistant taxonomic outlier Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA7
- PMID: 20107499
- PMCID: PMC2809737
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008842
Complete genome sequence of the multiresistant taxonomic outlier Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA7
Abstract
Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA7 is a non-respiratory human isolate from Argentina that is multiresistant to antibiotics. We first sequenced gyrA, gyrB, parC, parE, ampC, ampR, and several housekeeping genes and found that PA7 is a taxonomic outlier. We report here the complete sequence of the 6,588,339 bp genome, which has only about 95% overall identity to other strains. PA7 has multiple novel genomic islands and a total of 51 occupied regions of genomic plasticity. These islands include antibiotic resistance genes, parts of transposons, prophages, and a pKLC102-related island. Several PA7 genes not present in PAO1 or PA14 are putative orthologues of other Pseudomonas spp. and Ralstonia spp. genes. PA7 appears to be closely related to the known taxonomic outlier DSM1128 (ATCC9027). PA7 lacks several virulence factors, notably the entire TTSS region corresponding to PA1690-PA1725 of PAO1. It has neither exoS nor exoU and lacks toxA, exoT, and exoY. PA7 is serotype O12 and pyoverdin type II. Preliminary proteomic studies indicate numerous differences with PAO1, some of which are probably a consequence of a frameshift mutation in the mvfR quorum sensing regulatory gene.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
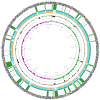
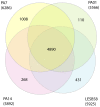
References
-
- Stover CK, Pham XQ, Erwin AL, Mizoguchi SD, Warrener P, et al. Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, an opportunistic pathogen. Nature. 2000;406:959–964. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

