Pea3 transcription factors and wnt1-induced mouse mammary neoplasia
- PMID: 20107508
- PMCID: PMC2809747
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008854
Pea3 transcription factors and wnt1-induced mouse mammary neoplasia
Abstract
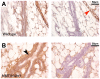
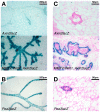
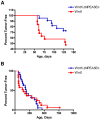
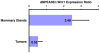
The role of the PEA3 subfamily of Ets transcription factors in breast neoplasia is controversial. Although overexpression of PEA3 (E1AF/ETV4), and of the related factors ERM (ETV5) and ER81 (ETV1), have been observed in human and mouse breast tumors, PEA3 factors have also been ascribed a tumor suppressor function. Here, we utilized the MMTV/Wnt1 mouse strain to further interrogate the role of PEA3 transcription factors in mammary tumorigenesis based on our previous observation that Pea3 is highly expressed in MMTV/Wnt1 mammary tumors. Pea3 expression in mouse mammary tissues was visualized using a Pea3(NLSlacZ) reporter strain. In normal mammary glands, Pea3 expression is predominantly confined to myoepithelial cells. Wnt1 transgene expression induced marked amplification of this cell compartment in nontumorous mammary glands, accompanied by an apparent increase in Pea3 expression. The pattern of Pea3 expression in MMTV/Wnt1 mammary glands recapitulated the cellular profile of activated beta-catenin/TCF signaling, which was visualized using both beta-catenin immunohistochemistry and the beta-catenin/TCF-responsive reporter Axin2(NLSlacZ). To test the requirement for PEA3 factors in Wnt1-induced tumorigenesis, we employed a mammary-targeted dominant negative PEA3 transgene, DeltaNPEA3En. Expression of DeltaNPEA3En delayed early-onset tumor formation in MMTV/Wnt1 virgin females (P = 0.03), suggesting a requirement for PEA3 factor function for Wnt1-driven tumor formation. Consistent with this observation, expression of the DeltaNPEA3En transgene was profoundly reduced in mammary tumors compared to nontumorous mammary glands from bigenic MMTV/Wnt1, MMTV/DeltaNPEA3En mice (P = 0.01). Our data provide the first description of Wnt1-mediated expansion of the Pea3-expressing myoepithelial compartment in nontumorous mammary glands. Consistent with this observation, mammary myoepithelium was selectively responsive to Wnt1. Together these data suggest the MMTV/Wnt1 strain as a potential model of basal breast cancer. Furthermore, this study provides evidence for a protumorigenic role of PEA3 factors in breast neoplasia, and supports targeting the PEA3 transcription factor family in breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Graves BJ, Petersen JM. Specificity within the ets family of transcription factors. Adv Cancer Res. 1998;75:1–55. - PubMed
-
- Sharrocks AD. The ETS-domain transcription factor family. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:827–837. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd T, Hassell JA. Role of Ets transcription factors in mammary gland development and oncogenesis. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2001;6:129–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

