Trace determination of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates: application in artificially polluted soil-carrots system
- PMID: 20107562
- PMCID: PMC2809018
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/404836
Trace determination of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates: application in artificially polluted soil-carrots system
Abstract
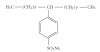
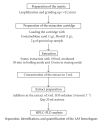
Surfactants are widely used in household and industrial products. The risk of incorporation of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates (LAS) from biosolids, wastewater, and fertilizers land application to the food chain is being assessed at present by the European Union. In the present work, a complete analytical method for LAS trace determination has been developed and successfully applied to LAS (C10-C13) uptake in carrot plants used as model. These carrots were grown in soil with the trace organics compounds added directly into the plant containers in pure substances form. LAS trace determination (mug kg(-1) dry matter) in carrots samples was achieved by Soxtec apparatus and high-performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. The methodology developed provides LAS determination at low detection limits (5 mug kg(-1) dry matter) for carrot sample (2 g dry matter) with good recoveries rate (>90%). Transfer of LAS has been followed into the various parts of the carrot plant. LAS are generally found in the carrot leaves and percentage transfer remains very low (0.02%).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Method for the simultaneous determination of the most problematic families of organic pollutants in compost and compost-amended soil.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010 May;397(1):277-285. doi: 10.1007/s00216-010-3509-y. Epub 2010 Mar 6. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010. PMID: 20213175
-
Determination of priority pollutants in aqueous samples by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction.Anal Chim Acta. 2013 Apr 22;773:60-67. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2013.02.032. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Anal Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23561907
-
Determination of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates in water samples by liquid chromatography-UV detection and confirmation by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.Talanta. 2005 Oct 15;67(4):686-95. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2005.03.011. Epub 2005 Apr 19. Talanta. 2005. PMID: 18970226
-
Probabilistic risk assessment for linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS) in sewage sludge used on agricultural soil.Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2007 Dec;49(3):245-59. doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2007.09.001. Epub 2007 Sep 19. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17967498 Review.
-
Linear alkylbenzene sulfonates (LAS) in sewage sludges, soils and sediments: analytical determination and environmental safety considerations.Int J Environ Anal Chem. 1986;26(3-4):279-93. doi: 10.1080/03067318608077120. Int J Environ Anal Chem. 1986. PMID: 3533808 Review.
Cited by
-
Qualitative and quantitative methods detection of SDS based on polyelectrolyte microcapsules.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 7;12(1):232. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-04343-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 34997163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rapaport RA, Eckhoff WS. Monitoring linear alkyl benzene sulfonate in the environment: 1973–1986. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry. 1990;9(10):1245–1257.
-
- Jensen J. Fate and effects of linear alkylbenzene sulphonates (LAS) in the terrestrial environment. The Science of the Total Environment. 1999;226(2-3):93–111. - PubMed
-
- Thoumelin G. Les Tensio-Actifs dans les Eaux Douces et Marines: Analyse, Comportement, Ecotoxicologie. Lille, France: Reperes Ocean; 1995.
-
- Marcomini A, Filipuzzi F, Giger W. Aromatic surfactants in laundry detergents and hard-surface cleaners: linear alkylbenzenesulphonates and alkylphenol polyethoxylates. Chemosphere. 1988;17(5):853–863.
-
- De Wolf W, Feijtel T. Terrestrial risk assessment for linear alkyl benzene sulfonate (LAS) in sludge-amended soils. Chemosphere. 1998;36(6):1319–1343. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

