New insights in the pathogenesis of atopic disease
- PMID: 20108533
- PMCID: PMC5685145
New insights in the pathogenesis of atopic disease
Abstract
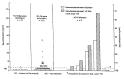
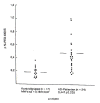
A causal link between the increasing environmental pollution and the fast spreading of allergic diseases is currently discussed. The exogenic and endogenic noxious agents contributing to the total environmental load are primarily acting through immunotoxic, sensitizing and neurotoxic mechanisms in animal experiments and in humans. Beside classic allergic-triggering factors (allergen potency, intermittent exposure to different allergen concentrations, presence of microbial bodies and sensitizing phenols), the adjuvant role of environmental pollutants gains increasing importance in allergy induction. Our therapy experience with more than 18.000 atopic eczema patients shows that beside allergic reactions pseudoallergic mechanisms through toxic environmental agents (formaldehyde, industrial and traffic smog, wood preservatives, microbial toxins, additive-rich food, nicotine, alcohol, pesticides, solvents, amalgam-heavy metals) are increasingly incriminated as causal factors for the complex symptomatology. The avoidance and elimination of such triggering factors before and during pregnancy and in early childhood may result in a significant decrease of the incidence of atopic diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Atopic Dermatitis Is a Barrier Issue, Not an Allergy Issue.Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2019 Nov;39(4):507-519. doi: 10.1016/j.iac.2019.07.005. Epub 2019 Aug 31. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2019. PMID: 31563185 Review.
-
Food allergy and atopic dermatitis: Prediction, progression, and prevention.Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2017 Dec;28(8):831-840. doi: 10.1111/pai.12831. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29117431 Review.
-
The allergic march: can we prevent allergies and asthma?Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2011 Jun;44(3):765-77, xi. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2011.03.006. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2011. PMID: 21621060 Review.
-
Early life environmental exposure in relation to new onset and remission of allergic diseases in school children: Polish Mother and Child Cohort Study.Allergy Asthma Proc. 2019 Sep 1;40(5):329-337. doi: 10.2500/aap.2019.40.4237. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2019. PMID: 31514791
-
Maternal smoking and environmental tobacco smoke exposure and the risk of allergic diseases in Japanese infants: the Osaka Maternal and Child Health Study.J Asthma. 2008 Nov;45(9):833-8. doi: 10.1080/02770900802339742. J Asthma. 2008. PMID: 18972305
Cited by
-
Hapten may play an important role in food allergen-related intestinal immune inflammation.N Am J Med Sci. 2011 Mar;3(3):103-6. doi: 10.4297/najms.2011.3103. N Am J Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 22540076 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrew WF. The importance of the total load in the control of allergic symptoms. Clin Ecology. 1987/88;3:145–148.
-
- Stickl H. Umweltwirkungen auf das Immunsystem. Acta med Austriaca. 1985;12:6–16. - PubMed
-
- Rousseaux CG. Immunologic responses that may follow exposure to chemicals. Clin Ecology. 1987;1:33–37.
-
- Schliköter H-W, Dolgner R. Luftverunreinigung und körpereigene Abwhr. Zentralbl Bakt Hyg I. Abt. Orig B. 1981;172:299–311. - PubMed
-
- Bozella B, et al. Cadmium, a metallic inhibitor of antibody mediated immunity. Environm Res. 1978;17:390–402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical