Mechano-transduction in periodontal ligament cells identifies activated states of MAP-kinases p42/44 and p38-stress kinase as a mechanism for MMP-13 expression
- PMID: 20109185
- PMCID: PMC2824740
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2121-11-10
Mechano-transduction in periodontal ligament cells identifies activated states of MAP-kinases p42/44 and p38-stress kinase as a mechanism for MMP-13 expression
Abstract
Background: Mechano-transduction in periodontal ligament (PDL) cells is crucial for physiological and orthodontic tooth movement-associated periodontal remodelling. On the mechanistic level, molecules involved in this mechano-transduction process in PDL cells are not yet completely elucidated.
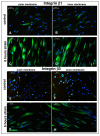
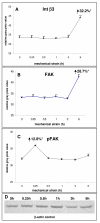
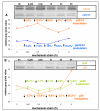
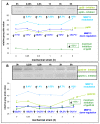
Results: In the present study we show by western blot (WB) analysis and/or indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) that mechanical strain modulates the amount of the matrix metalloproteinase MMP-13, and induces non-coherent modulation in the amount and activity of signal transducing molecules, such as FAK, MAP-kinases p42/44, and p38 stress kinase, suggesting their mechanistic role in mechano-transduction. Increase in the amount of FAK occurs concomitant with increased levels of the focal contact integrin subunits beta3 and beta1, as indicated by WB or optionally by IIF. By employing specific inhibitors, we further identified p42/44 and p38 in their activated, i.e. phosphorylated state responsible for the expression of MMP-13. This finding may point to the obedience in the expression of this MMP as extracellular matrix (ECM) remodelling executioner from the activation state of mechano-transducing molecules. mRNA analysis by pathway-specific RT-profiler arrays revealed up- and/or down-regulation of genes assigning to MAP-kinase signalling and cell cycle, ECM and integrins and growth factors. Up-regulated genes include for example focal contact integrin subunit alpha3, MMP-12, MAP-kinases and associated kinases, and the transcription factor c-fos, the latter as constituent of the AP1-complex addressing the MMP-13 promotor. Among others, genes down-regulated are those of COL-1 and COL-14, suggesting that strain-dependent mechano-transduction may transiently perturbate ECM homeostasis.
Conclusions: Strain-dependent mechano-/signal-transduction in PDL cells involves abundance and activity of FAK, MAP-kinases p42/44, and p38 stress kinase in conjunction with the amount of MMP-13, and integrin subunits beta1 and beta3. Identifying the activated state of p42/44 and p38 as critical for MMP-13 expression may indicate the mechanistic contribution of mechano-transducing molecules on executioners of ECM homeostasis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fluid shear stress regulates metalloproteinase-1 and 2 in human periodontal ligament cells: involvement of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and P38 signaling pathways.J Biomech. 2012 Sep 21;45(14):2368-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2012.07.013. Epub 2012 Aug 3. J Biomech. 2012. PMID: 22863019 Clinical Trial.
-
Fluid shear stress stimulates osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways.J Periodontol. 2014 Dec;85(12):1806-13. doi: 10.1902/jop.2014.140244. J Periodontol. 2014. PMID: 25186781
-
Mechanical force enhances MMP-2 activation via p38 signaling pathway in human retinal pigment epithelial cells.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009 Nov;247(11):1477-86. doi: 10.1007/s00417-009-1135-1. Epub 2009 Jul 10. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009. PMID: 19590887
-
Extracellular Matrix Remodelling of the Periodontium under Orthodontic Force.Chin J Dent Res. 2024 Jun 28;27(2):121-131. doi: 10.3290/j.cjdr.b5459583. Chin J Dent Res. 2024. PMID: 38953477 Review.
-
Integrin and Its Associated Proteins as a Mediator for Mechano-Signal Transduction.Biomolecules. 2025 Jan 23;15(2):166. doi: 10.3390/biom15020166. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001469 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechano-regulation of collagen biosynthesis in periodontal ligament.J Prosthodont Res. 2014 Oct;58(4):193-207. doi: 10.1016/j.jpor.2014.08.003. Epub 2014 Oct 11. J Prosthodont Res. 2014. PMID: 25311991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spinal facet joint biomechanics and mechanotransduction in normal, injury and degenerative conditions.J Biomech Eng. 2011 Jul;133(7):071010. doi: 10.1115/1.4004493. J Biomech Eng. 2011. PMID: 21823749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Tensile Frequency on the Osteogenic Differentiation of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Jul 2;15:5957-5971. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S368394. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35811779 Free PMC article.
-
Endotoxins potentiate COX-2 and RANKL expression in compressed PDL cells.Clin Oral Investig. 2013 Dec;17(9):2041-8. doi: 10.1007/s00784-013-0928-0. Epub 2013 Feb 8. Clin Oral Investig. 2013. PMID: 23392729
-
Periodontal cell mechanotransduction.Open Biol. 2018 Aug 16;8(9):180053. doi: 10.1098/rsob.180053. Open Biol. 2018. PMID: 30209038 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

