Mitotic functions of kinesin-5
- PMID: 20109572
- PMCID: PMC2844466
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.01.019
Mitotic functions of kinesin-5
Abstract
In all eukaryotic cells, molecular motor proteins play essential roles in spindle assembly and function. The homotetrameric kinesin-5 motors in particular generate outward forces that establish and maintain spindle bipolarity and contribute to microtubule flux. Cell-cycle dependent phosphorylation of kinesin-5 motors regulates their localization to the mitotic spindle. Analysis of live cells further shows that kinesin-5 motors are highly dynamic in the spindle. Understanding the interactions of kinesin-5 motors with microtubules and other spindle proteins is likely to broaden the documented roles of kinesin-5 motors during cell division.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
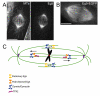
References
-
- Bannigan A, Scheible W, Lukowitz W, Fagerstrom C, Wadsworth P, Somerville C, Baskin TI. A conserved role for kinesin-5 in plant mitosis. J. Cell Sci. 2007;120:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Blangy A, Arnaud L, Nigg EA. Phosphorylation by p34cdc2 protein kinase regulates binding of the kinesin related motor HsEg5 to the dynactin subunit p150glued. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:19418–19424. - PubMed
-
- Blangy A, Lane HA, d’Herin P, Harper M, Kress M, Nigg EA. Phosphorylation by p34cdc2 regulates spindle association of human Eg5, a kinesin related motor essential for bipolar spindle formation in vivo. Cell. 1995;83:1159–1169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

