Biocompatibility of a synthetic extracellular matrix on immortalized vocal fold fibroblasts in 3-D culture
- PMID: 20109588
- PMCID: PMC2883010
- DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2010.01.032
Biocompatibility of a synthetic extracellular matrix on immortalized vocal fold fibroblasts in 3-D culture
Abstract
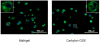
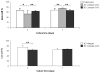
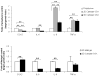
In order to promote wound repair and induce tissue regeneration, an engineered hyaluronan (HA) hydrogel - Carbylan GSX, which contains di(thiopropionyl) bishydrazide-modified hyaluronic acid, di(thiopropionyl) bishydrazide-modified gelatin and polyethylene glycol diacrylate - has been developed for extracellular matrix (ECM) defects of the superficial and middle layers of the lamina propria. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the biocompatibility of Carbylan GSX in a previously established immortalized human vocal fold fibroblast (hVFF) cell line prior to human clinical trials. Immortalized hVFF proliferation, viability, apoptosis and transcript analysis for both ECM constituents and inflammatory markers were measured for two-dimensional and three-dimensional (3-D) culture conditions. There were no significant differences in morphology, cell marker protein expression, proliferation, viability and apoptosis of hVFF cultured with Carbylan GSX compared to Matrigel, a commercial 3-D control, after 1 week. Gene expression levels for fibromodulin, transforming growth factor-beta1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha were similar between Carbylan GSX and Matrigel. Fibronectin, hyaluronidase 1 and cyclooxygenase II expression levels were induced by Carbylan GSX, whereas interleukins 6 and 8, Col I and hyaluronic acid synthase 3 expression levels were decreased by Carbylan GSX. This investigation demonstrates that Carbylan GSX may serve as a natural biomaterial for tissue-engineering of human vocal folds.
Copyright 2010 Acta Materialia Inc. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in wound repair in human vocal fold fibroblasts.Laryngoscope. 2010 Sep;120(9):1819-25. doi: 10.1002/lary.21037. Laryngoscope. 2010. PMID: 20715091 Free PMC article.
-
Vocal fold tissue repair in vivo using a synthetic extracellular matrix.Tissue Eng. 2006 Aug;12(8):2171-80. doi: 10.1089/ten.2006.12.2171. Tissue Eng. 2006. PMID: 16968158
-
Effect of a synthetic extracellular matrix on vocal fold lamina propria gene expression in early wound healing.Tissue Eng. 2006 Nov;12(11):3201-7. doi: 10.1089/ten.2006.12.3201. Tissue Eng. 2006. PMID: 17518634
-
Response of fibroblasts to transforming growth factor-β1 on two-dimensional and in three-dimensional hyaluronan hydrogels.Tissue Eng Part A. 2012 Dec;18(23-24):2528-38. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2012.0094. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012. PMID: 22734649 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in our understanding of the Reinke space.Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005 Jun;13(3):148-51. doi: 10.1097/01.moo.0000163450.90455.fb. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005. PMID: 15908811 Review.
Cited by
-
Vocal fold myofibroblast profile of scarring.Laryngoscope. 2016 Mar;126(3):E110-7. doi: 10.1002/lary.25581. Epub 2015 Sep 7. Laryngoscope. 2016. PMID: 26344050 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronic acid hydrogels for vocal fold wound healing.Biomatter. 2013 Jan-Mar;3(1):e23799. doi: 10.4161/biom.23799. Epub 2013 Jan 1. Biomatter. 2013. PMID: 23507923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Hyaluronic Acid and Hyaluronic Acid-based Hydrogels for Vocal Fold Tissue Engineering.J Voice. 2017 Jul;31(4):416-423. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2016.11.014. Epub 2017 Mar 2. J Voice. 2017. PMID: 28262503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Controlling the fibroblastic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via the combination of fibrous scaffolds and connective tissue growth factor.Tissue Eng Part A. 2011 Nov;17(21-22):2773-85. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2011.0219. Epub 2011 Aug 2. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011. PMID: 21689062 Free PMC article.
-
Human embryonic stem cell-derived epithelial cells in a novel in vitro model of vocal mucosa.Tissue Eng Part A. 2013 Oct;19(19-20):2233-41. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2012.0744. Epub 2013 Jun 26. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013. PMID: 23672433 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gray SD, Pignatari SS, Harding P. Morphologic ultrastructure of anchoring fibers in normal vocal fold basement membrane zone. J Voice. 1994;8(1):48–52. - PubMed
-
- Pawlak AS, Hammond T, Hammond E, Gray SD. Immunocytochemical study of proteoglycans in vocal folds. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1996;105(1):6–11. - PubMed
-
- Hammond TH, Zhou R, Hammond EH, Pawlak A, Gray SD. The intermediate layer: a morphologic study of the elastin and hyaluronic acid constituents of normal human vocal folds. J Voice. 1997;11(1):59–66. - PubMed
-
- Gray SD, Titze IR, Alipour F, Hammond TH. Biomechanical and histologic observations of vocal fold fibrous proteins. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2000;109(1):77–85. - PubMed
-
- Chan RW, Titze IR. Viscoelastic shear properties of human vocal fold mucosa: theoretical characterization based on constitutive modeling. J Acoust Soc Am. 2000;107(1):565–580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

