MicroRNAs expression signatures are associated with lineage and survival in acute leukemias
- PMID: 20110180
- PMCID: PMC2829339
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2009.12.010
MicroRNAs expression signatures are associated with lineage and survival in acute leukemias
Abstract
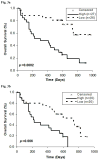
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small ( approximately 22 nucleotide) non-coding RNAs whose altered expression has been associated with various types of cancers, including leukemia. In the present study, we conducted a quantitative PCR (qPCR) analysis of expression of 23 human precursor miRNAs in bone marrow specimens of 85 Chinese primary leukemia patients, including 53 acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and 32 acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cases. We show that 16 miRNAs were differentially expressed between AMLs and ALLs. Of them, eight were previously reported (i.e., miR-23a, miR-27a/b, miR-128a, miR-128b, miR-221, miR-222, miR-223, and let-7b) and eight were newly identified (i.e., miR-17, miR-20a, miR-29a/c, miR-29b, miR-146a, miR-150, miR-155, and miR-196b). More importantly, through correlating miRNA expression signatures with outcome of patients, we further show that expression signatures of a group of miRNAs are associated with overall survival of patients. Of them, three (i.e., miR-146a, miR-181a/c, and miR-221), five (i.e., miR-25, miR-26a, miR-29b, miR-146a, and miR-196b), and three (i.e., miR-26a, miR-29b, and miR-146a) miRNAs are significantly associated with overall survival (P<0.05) of the 32 ALL, 53 AML, and 40 non-M3 AML patients, respectively. Particularly, the expression signature of miR-146a is significantly inversely correlated with overall survival of both ALL and AML patients. The prognostic significance of miR-146a in AML has been confirmed further in an independent study of 61 Chinese new AML patient samples. We also identified 622 putative target genes of miR-146a that are predicted by at least three out of the five major prediction programs (i.e., TragetScan, PicTar, miRanda, miRBase Targets, and PITA). Through gene ontology analysis, we found that these genes were particularly enriched (2- to 9-fold higher than expected by chance) in the GO categories of "negative regulation of biology processes," "negative regulation of cellular processes," "apoptosis," and "cell cycle," which may be related to the association of miR-146a with poor survival.
2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
MicroRNA expression signatures accurately discriminate acute lymphoblastic leukemia from acute myeloid leukemia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Dec 11;104(50):19971-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709313104. Epub 2007 Dec 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 18056805 Free PMC article.
-
Functional implications of microRNAs in acute myeloid leukemia by integrating microRNA and messenger RNA expression profiling.Cancer. 2011 Oct 15;117(20):4696-706. doi: 10.1002/cncr.26096. Epub 2011 Mar 31. Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21455993 Free PMC article.
-
High bone marrow miR-19b level predicts poor prognosis and disease recurrence in de novo acute myeloid leukemia.Gene. 2018 Jan 15;640:79-85. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.10.034. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29032147
-
Meta-analysis of microRNA profiling data does not reveal a consensus signature for B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Gene. 2022 May 5;821:146211. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.146211. Epub 2022 Feb 5. Gene. 2022. PMID: 35134470 Review.
-
MicroRNA as a diagnostic biomarker in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia; systematic review, meta-analysis and recommendations.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2019 Apr;136:70-78. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2019.02.008. Epub 2019 Feb 23. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2019. PMID: 30878131
Cited by
-
The pathological role and prognostic impact of miR-181 in acute myeloid leukemia.Cancer Genet. 2015 May;208(5):225-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2014.12.006. Epub 2015 Jan 7. Cancer Genet. 2015. PMID: 25686674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hsa-miR-196a2 functional SNP is associated with severe toxicity after platinum-based chemotherapy of advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer patients in a Chinese population.J Clin Lab Anal. 2012 Nov;26(6):441-6. doi: 10.1002/jcla.21544. J Clin Lab Anal. 2012. PMID: 23143626 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Non random distribution of genomic features in breakpoint regions involved in chronic myeloid leukemia cases with variant t(9;22) or additional chromosomal rearrangements.Mol Cancer. 2010 May 25;9:120. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-120. Mol Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20500819 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical impact of circulating microRNAs as blood-based marker in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Tumour Biol. 2016 Aug;37(8):10571-6. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-4948-7. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26857279
-
MiR-223-3p in Cancer Development and Cancer Drug Resistance: Same Coin, Different Faces.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 26;25(15):8191. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158191. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125761 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:522–531. - PubMed
-
- Wu W, Sun M, Zou GM, Chen J. MicroRNA and cancer: Current status and prospective. Int J Cancer. 2007;120:953–960. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

