Incorporating sequence quality data into alignment improves DNA read mapping
- PMID: 20110255
- PMCID: PMC2853142
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq010
Incorporating sequence quality data into alignment improves DNA read mapping
Abstract
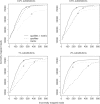
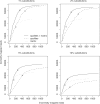
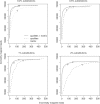
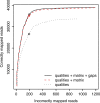
New DNA sequencing technologies have achieved breakthroughs in throughput, at the expense of higher error rates. The primary way of interpreting biological sequences is via alignment, but standard alignment methods assume the sequences are accurate. Here, we describe how to incorporate the per-base error probabilities reported by sequencers into alignment. Unlike existing tools for DNA read mapping, our method models both sequencer errors and real sequence differences. This approach consistently improves mapping accuracy, even when the rate of real sequence difference is only 0.2%. Furthermore, when mapping Drosophila melanogaster reads to the Drosophila simulans genome, it increased the amount of correctly mapped reads from 49 to 66%. This approach enables more effective use of DNA reads from organisms that lack reference genomes, are extinct or are highly polymorphic.
Figures
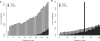
References
-
- Malde K. The effect of sequence quality on sequence alignment. Bioinformatics. 2008;24:897–900. - PubMed
-
- Na JC, Roh K, Apostolico A, Park K. Alignment of biological sequences with quality scores. Int. J. Bioinformatics Res. Appl. 2009;5:97–113. - PubMed
-
- Millar CD, Huynen L, Subramanian S, Mohandesan E, Lambert DM. New developments in ancient genomics. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008;23:386–393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

