Binding of aminoglycoside antibiotics to helix 69 of 23S rRNA
- PMID: 20110260
- PMCID: PMC2875026
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp1253
Binding of aminoglycoside antibiotics to helix 69 of 23S rRNA
Abstract
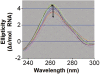
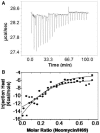
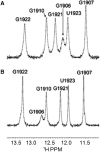
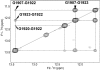
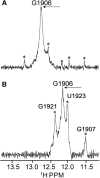
Aminoglycosides antibiotics negate dissociation and recycling of the bacterial ribosome's subunits by binding to Helix 69 (H69) of 23S rRNA. The differential binding of various aminoglycosides to the chemically synthesized terminal domains of the Escherichia coli and human H69 has been characterized using spectroscopy, calorimetry and NMR. The unmodified E. coli H69 hairpin exhibited a significantly higher affinity for neomycin B and tobramycin than for paromomycin (K(d)s = 0.3 +/- 0.1, 0.2 +/- 0.2 and 5.4 +/- 1.1 microM, respectively). The binding of streptomycin was too weak to assess. In contrast to the E. coli H69, the human 28S rRNA H69 had a considerable decrease in affinity for the antibiotics, an important validation of the bacterial target. The three conserved pseudouridine modifications (Psi1911, Psi1915, Psi1917) occurring in the loop of the E. coli H69 affected the dissociation constant, but not the stoichiometry for the binding of paromomycin (K(d) = 2.6 +/- 0.1 microM). G1906 and G1921, observed by NMR spectrometry, figured predominantly in the aminoglycoside binding to H69. The higher affinity of the E. coli H69 for neomycin B and tobramycin, as compared to paromomycin and streptomycin, indicates differences in the efficacy of the aminoglycosides.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structure modulation of helix 69 from Escherichia coli 23S ribosomal RNA by pseudouridylations.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Apr;42(6):3971-81. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1329. Epub 2013 Dec 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24371282 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudouridine modifications influence binding of aminoglycosides to helix 69 of bacterial ribosomes.Org Biomol Chem. 2017 Oct 18;15(40):8535-8543. doi: 10.1039/c7ob02147j. Org Biomol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28959821 Free PMC article.
-
Indigenous and acquired modifications in the aminoglycoside binding sites of Pseudomonas aeruginosa rRNAs.RNA Biol. 2013 Aug;10(8):1324-32. doi: 10.4161/rna.25984. Epub 2013 Aug 5. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23948732 Free PMC article.
-
Thermodynamics of aminoglycoside-rRNA recognition.Biopolymers. 2003 Sep;70(1):58-79. doi: 10.1002/bip.10411. Biopolymers. 2003. PMID: 12925993 Review.
-
An expanding view of aminoglycoside-nucleic acid recognition.Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 2006;60:251-302. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2318(06)60006-1. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16750445 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Ligand- and pH-induced conformational changes of RNA domain helix 69 revealed by 2-aminopurine fluorescence.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2012 Nov 26;51(48):12095-8. doi: 10.1002/anie.201206000. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2012. PMID: 23097282 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Overproduction of gentamicin B in industrial strain Micromonospora echinospora CCTCC M 2018898 by cloning of the missing genes genR and genS.Metab Eng Commun. 2019 Jul 24;9:e00096. doi: 10.1016/j.mec.2019.e00096. eCollection 2019 Dec. Metab Eng Commun. 2019. PMID: 31720212 Free PMC article.
-
4'-O-substitutions determine selectivity of aminoglycoside antibiotics.Nat Commun. 2014;5:3112. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4112. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 24473108 Free PMC article.
-
Toward inclusive therapy with CFTR modulators: Progress and challenges.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2017 Nov;52(S48):S4-S14. doi: 10.1002/ppul.23773. Epub 2017 Sep 7. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2017. PMID: 28881097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay of the bacterial ribosomal A-site, S12 protein mutations and paromomycin binding: a molecular dynamics study.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 7;9(11):e111811. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111811. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25379961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moazed D, Noller HF. Interaction of antibiotics with functional sites in 16S ribosomal RNA. Nature. 1987;327:389–394. - PubMed
-
- Magnet S, Blanchard JS. Molecular insights into aminoglycoside action and resistance. Chem. Rev. 2005;105:477–498. - PubMed
-
- Tor Y. The ribosomal A-site as an inspiration for the design of RNA binders. Biochimie. 2006;88:1045–1051. - PubMed
-
- Misumi M, Nishimura T, Komai T, Tanaka N. Interaction of kanamycin and related antibiotics with the large subunit of ribosomes and the inhibition of translocation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1978;84:358–365. - PubMed
-
- Campuzano S, Vazquez D, Modolell, J Functional interaction of neomycin B and related antibiotics with 30S and 50S ribosomal subunits. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1979;87:960–966. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

