Androgen receptor interacts with telomeric proteins in prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 20110352
- PMCID: PMC2856254
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.098798
Androgen receptor interacts with telomeric proteins in prostate cancer cells
Abstract
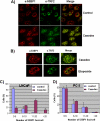
The telomeric complex, shelterin, plays a critical role in protecting chromosome ends from erosion, and disruption of these complexes can lead to chromosomal instability culminating in cell death or malignant transformation. We reported previously that dominant-negative mutants of one of the telomeric proteins called TIN2 cause death of androgen receptor (AR)-negative but not AR-positive prostate cancer cells, raising the question of a possible role of AR in the structural stability of telomeric complexes. Consistent with this possibility, in the present study, we observed that the AR antagonist Casodex (bicalutamide) disrupted telomeric complexes in AR-positive LNCaP cells but not in AR-negative PC-3 cells. Immunofluorescent studies revealed colocalization of TIN2 and AR. Reciprocal immunoprecipitation studies showed association of AR with telomeric proteins. Furthermore, telomeric proteins were overexpressed in prostate cancer cells compared with normal prostate epithelial cells, and sucrose density gradient analysis showed co-sedimentation of AR with telomeric proteins in a shelterin-like mega complex. Together, these observations suggest an allosteric role of AR in telomere complex stability in prostate cancer cells and suggest that AR-antagonist Casodex-mediated cell death may be due to telomere complex disruption.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structural and functional association of androgen receptor with telomeres in prostate cancer cells.Aging (Albany NY). 2013 Jan;5(1):3-17. doi: 10.18632/aging.100524. Aging (Albany NY). 2013. PMID: 23363843 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of androgen receptor-mediated transcription by RPB5 binding protein URI/RMP.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Sep;31(17):3639-52. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05429-11. Epub 2011 Jul 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21730289 Free PMC article.
-
Prohibitin and the SWI/SNF ATPase subunit BRG1 are required for effective androgen antagonist-mediated transcriptional repression of androgen receptor-regulated genes.Carcinogenesis. 2008 Sep;29(9):1725-33. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgn117. Epub 2008 May 16. Carcinogenesis. 2008. PMID: 18487222 Free PMC article.
-
Shelterin proteins and cancer.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(8):3085-90. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.8.3085. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015. PMID: 25921101 Review.
-
[Research progress on telomere binding proteins].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2004 Nov;33(6):469-73. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2004.06.001. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2004. PMID: 15586400 Review. Chinese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Melanoma of non-sun exposed skin in a man with previous prostate cancer: recognition of a recently confirmed association.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2014 Jun;4(1):125-9. doi: 10.1007/s13555-014-0045-2. Epub 2014 Feb 22. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2014. PMID: 24563423 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of TERF1 expression in prostate cancer.J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2021 Sep 6;33(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s43046-021-00082-4. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2021. PMID: 34486082
-
Association between melanoma and exposure to sex hormones in puberty: A possible window of susceptibility (Review).Mol Clin Oncol. 2021 Apr;14(4):66. doi: 10.3892/mco.2021.2228. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Mol Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33680457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of human protein-protein interaction by a mixed Bayesian model and its application to exploring underlying cancer-related pathway crosstalk.J R Soc Interface. 2011 Apr 6;8(57):555-67. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2010.0384. Epub 2010 Oct 13. J R Soc Interface. 2011. PMID: 20943681 Free PMC article.
-
The potential for chemical mixtures from the environment to enable the cancer hallmark of sustained proliferative signalling.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Jun;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S38-60. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv030. Carcinogenesis. 2015. PMID: 26106143 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rodier F., Kim S. H., Nijjar T., Yaswen P., Campisi J. (2005) Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 37, 977–990 - PubMed
-
- Kim S. H., Beausejour C., Davalos A. R., Kaminker P., Heo S. J., Campisi J. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 43799–43804 - PubMed
-
- Liu D., Safari A., O'Connor M. S., Chan D. W., Laegeler A., Qin J., Songyang Z. (2004) Nat. Cell Biol. 6, 673–680 - PubMed
-
- Ye J. Z., Donigian J. R., van Overbeek M., Loayza D., Luo Y., Krutchinsky A. N., Chait B. T., de Lange T. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 47264–47271 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

