Spontaneous remission of nephrotic syndrome in idiopathic membranous nephropathy
- PMID: 20110379
- PMCID: PMC2844306
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2009080861
Spontaneous remission of nephrotic syndrome in idiopathic membranous nephropathy
Abstract
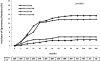
Spontaneous remission is a well known characteristic of idiopathic membranous nephropathy, but contemporary studies describing predictors of remission and long-term outcomes are lacking. We conducted a retrospective, multicenter cohort study of 328 patients with nephrotic syndrome resulting from idiopathic membranous nephropathy that initially received conservative therapy. Spontaneous remission occurred in 104 (32%) patients: proteinuria progressively declined after diagnosis until remission of disease at 14.7 +/- 11.4 months. Although spontaneous remission was more frequent with lower levels of baseline proteinuria, it also frequently occurred in patients with massive proteinuria: 26% among those with baseline proteinuria 8 to 12 g/24 h and 22% among those with proteinuria >12 g/24 h. Baseline serum creatinine and proteinuria, treatment with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor antagonists, and a >50% decline of proteinuria from baseline during the first year of follow-up were significant independent predictors for spontaneous remission. Only six patients (5.7%) experienced a relapse of nephrotic syndrome. The incidence of death and ESRD were significantly lower among patients with spontaneous remission. In conclusion, spontaneous remission is common among patients with nephrotic syndrome resulting from membranous nephropathy and carries a favorable long-term outcome with a low incidence of relapse. A decrease in proteinuria >50% from baseline during the first year predicts spontaneous remission.
Figures
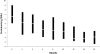
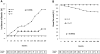
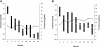
Comment in
-
Idiopathic membranous nephropathy: getting better by itself.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010 Apr;21(4):551-2. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010020185. Epub 2010 Mar 18. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20299357 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fervenza FC, Sethi S, Specks U: Idiopathic membranous nephropathy: Diagnosis and treatment. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3: 905– 919, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Cattran DC: Idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int 59: 1983– 1994, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Rivera F, López-Gómez JM, Pérez García R: Clinicopathological correlations of renal pathology in Spain. Kidney Int 66: 898– 904, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Coggins CH. for the Collaborative Study of the Adult Idiopathic Nephrotic Syndrome A controlled study of short-term prednisone treatment in adults with membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med 301: 1301– 1306, 1979 - PubMed
-
- Ponticelli C, Zucchelli P, Passerini P, Cagnoli L, Cesana B, Pozzi C, Pasquali S, Imbasciati E, Grassi C, Redaelli B, Sasdelli M, Locatelli F: A randomized trial of methylprednisone and chlorambucil in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med 320: 8– 13, 1989 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

