Kidneys of Alb/TGF-beta1 transgenic mice are deficient in retinoic acid and exogenous retinoic acid shows dose-dependent toxicity
- PMID: 20110732
- PMCID: PMC2865400
- DOI: 10.1159/000276587
Kidneys of Alb/TGF-beta1 transgenic mice are deficient in retinoic acid and exogenous retinoic acid shows dose-dependent toxicity
Abstract
Background: Alb/TGF-beta(1) transgenic mice overexpress active transforming growth factor-beta(1) (TGF-beta(1)) in the liver, leading to increased circulating levels of the cytokine and progressive renal fibrosis. This study was designed to explore if exogenous all-trans retinoic acid (tRA) prevents renal fibrosis in this animal model.
Methods: The retinoid profile in kidney and liver of wild-type and Alb/TGF-beta(1) transgenic mice was examined by high-performance liquid chromatography and slow-release pellets containing different amounts of tRA were implanted subcutaneously to treat the Alb/TGF-beta(1) transgenic mice, starting at 1 week of age; mice were sacrificed 2 weeks later.
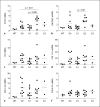
Results: Kidneys of 3-week-old wild-type mice had abundant tRA, which was completely absent in kidneys of the transgenic mice. Low doses of tRA (6-10.7 mg/kg/day) failed to affect renal fibrosis although it tended to suppress the mRNA expression of some molecular markers of fibrosis and retinal dehydrogenase 2 (RALDH2), a gene encoding a key tRA-synthesising enzyme. These tendencies disappeared, mortality tended to increase and RALDH2 and connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) mRNAs significantly increased in the medium-dose group (12.7-18.8 mg/kg/day). High doses (20.1-27.4 mg/kg/day) showed even higher toxicity with increased renal fibrosis and significant mortality.
Conclusions: Alb/TGF-beta(1) transgenic mice are characterised by depletion of endogenous renal tRA. Exogenous tRA dose-dependently increases mortality and kidney fibrosis, which is associated with dose-dependent regulation of renal RALDH2 and CTGF mRNA expression.
Copyright 2010 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures


References
-
- Feehally J, Floege J, Johnson RJ. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, ed 3, revised. London: Mosby; 2007.
-
- Xu Q, Lucio-Cazana J, Kitamura M, Ruan X, Fine LG, Norman J. Retinoids in nephrology: promises and pitfalls. Kidney Int. 2004;66:2119–2131. - PubMed
-
- Daly TJ, Weston WL. Retinoid effects on fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis in vitro and on fibrotic disease in vivo. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;15:900–902. - PubMed
-
- Redlich CA, Delisser HM, Elias JA. Retinoic acid inhibition of transforming growth factor-β-induced collagen production by human lung fibroblasts. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1995;12:287–295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

