Target gene context influences the transcriptional requirement for the KAT3 family of CBP and p300 histone acetyltransferases
- PMID: 20110770
- PMCID: PMC2829352
- DOI: 10.4161/epi.5.1.10449
Target gene context influences the transcriptional requirement for the KAT3 family of CBP and p300 histone acetyltransferases
Abstract
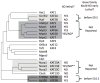
One general principle of gene regulation is that DNA-binding transcription factors modulate transcription by recruiting cofactors that modify histones and chromatin structure. A second implicit principle is that a particular cofactor is necessary at all the target genes where the cofactor is recruited. Increasingly, these principles do not appear to be absolute, as experimentally defined relationships between transcription, cofactors and chromatin modification grow in complexity. The KAT3 histone acetyltransferases CREB binding protein (CBP) and p300 have at least 400 interacting protein partners, thereby acting as hubs in gene regulatory networks. Studies using mutant primary cells indicate that the occurrence of CBP and p300 at any given target gene sometimes correlates with, rather than dictates transcription. This suggests that there are unexpected levels of redundancy between CBP/p300 and other unrelated coactivators, or that CBP/p300 recruitment may sometimes be coincidental. A transcription factor may therefore recruit the same group of coactivators as part of its "toolbox", but it is the characteristics of the individual target gene that determine which coactivation "tools" are required for its transcription.
Figures
References
-
- Spiegelman BM, Heinrich R. Biological control through regulated transcriptional coactivators. Cell. 2004;119:157–67. - PubMed
-
- Kasper LH, Brindle PK. Mammalian gene expression program resiliency: the roles of multiple coactivator mechanisms in hypoxia-responsive transcription. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:142–6. - PubMed
-
- Rosenfeld MG, Lunyak VV, Glass CK. Sensors and signals: a coactivator/corepressor/epigenetic code for integrating signal-dependent programs of transcriptional response. Genes Dev. 2006;20:1405–28. - PubMed
-
- Ptashne M. Words. Curr Biol. 2007;17:R533–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
