JNK contributes to Hif-1alpha regulation in hypoxic neurons
- PMID: 20110876
- PMCID: PMC6256924
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules15010114
JNK contributes to Hif-1alpha regulation in hypoxic neurons
Abstract
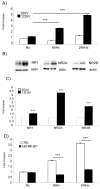
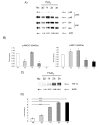
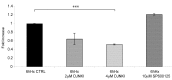
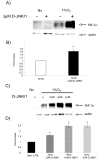
Hypoxia is an established factor of neurodegeneration. Nowadays, attention is directed at understanding how alterations in the expression of stress-related signaling proteins contribute to age dependent neuronal vulnerability to injury. The purpose of this study was to investigate how Hif-1alpha, a major neuroprotective factor, and JNK signaling, a key pathway in neurodegeneration, relate to hypoxic injury in young (6DIV) and adult (12DIV) neurons. We could show that in young neurons as compared to mature ones, the protective factor Hif-1alpha is more induced while the stress protein phospho-JNK displays lower basal levels. Indeed, changes in the expression levels of these proteins correlated with increased vulnerability of adult neurons to hypoxic injury. Furthermore, we describe for the first time that treatment with the D-JNKI1, a JNK-inhibiting peptide, rescues adult hypoxic neurons from death and contributes to Hif-1alpha upregulation, probably via a direct interaction with the Hif-1alpha protein.
Figures


References
-
- Lu T., Pan Y., Kao S.Y., Li C., Kohane I., Chan J., Yankner B.A. Gene regulation and DNA damage in the ageing human brain. Nature. 2004;429:883–891. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

