Identification and comparative quantification of bio-active phthalides in essential oils from si-wu-tang, fo-shou-san, radix angelica and rhizoma chuanxiong
- PMID: 20110895
- PMCID: PMC6257054
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules15010341
Identification and comparative quantification of bio-active phthalides in essential oils from si-wu-tang, fo-shou-san, radix angelica and rhizoma chuanxiong
Abstract
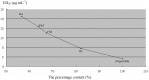
Phthalides are important bio-active constituents in Si-Wu-Tang and Fo-Shou-San, two commonly used Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) combined prescriptions mainly derived from Radix Angelica and Rhizoma Chuanxiong. In this paper, the contents of eight phthalides, including Z-ligustilide, E-ligustilide, Z-butylenephthalide, E-butylene-phthalide, 3-butylphthalide, neocnidilide and senkyunolide A were determined or estimated by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The results showed GC-MS was a simple, rapid, and high sensitive method for analyzing phthalides in Si-Wu-Tang, Fo-Shou-San, Radix Angelica and Rhizoma Chuanxiong, and the extractable contents of each phthalides including Z-ligustilide, E-ligustilide, Z-butylenephthalide, etc. varied after Radix Angelica, Rhizoma Chuanxiong were combined into a formulation, such as Si-Wu-Tang and Fo-Shou-San. Furthermore, inhibition activity of essential oils from Si-Wu-Tang, Fo-Shou-San, Radix Angelica and Rhizoma Chuanxiong on uterine contraction was tested in an in vitro assay, and the results showed that the activity of the essential oil is higher as the content of the phthalides increase, which demonstrated that phthalides are possibly main active components inhibiting mice uterine contraction in vitro. All of the results suggested that comparative analysis of chemical components and pharmacological activities of each herb and formula is possibly helpful to elucidate the active components in traditional Chinese medicine, and to reveal the compatibility mechanism of TCM formulae.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of main aromatic acids and phthalides in Angelicae Sinensis Radix, Chuanxiong Rhizoma, and Fo-Shou-San by a validated UHPLC-TQ-MS/MS.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Oct;99:45-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2014.07.007. Epub 2014 Jul 11. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 25061713
-
[Comparative Study on Volatile Oil Composition of Chuanxiong Rhizoma, Angelicae Sinensis Radix and Ligustici Rhizoma et Radix].Zhong Yao Cai. 2015 Jun;38(6):1212-6. Zhong Yao Cai. 2015. PMID: 26762063 Chinese.
-
Importance of wine-treated Angelica Sinensis Radix in Si Wu Tang, a traditional herbal formula for treating women's ailments.Planta Med. 2013 May;79(7):533-7. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1328261. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Planta Med. 2013. PMID: 23457023
-
Phthalides: Distribution in Nature, Chemical Reactivity, Synthesis, and Biological Activity.Prog Chem Org Nat Prod. 2017;104:127-246. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-45618-8_2. Prog Chem Org Nat Prod. 2017. PMID: 28160212 Review.
-
The analysis of Radix Angelicae Sinensis (Danggui).J Chromatogr A. 2009 Mar 13;1216(11):1991-2001. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2008.07.033. Epub 2008 Jul 18. J Chromatogr A. 2009. PMID: 18667208 Review.
Cited by
-
A new high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination and distribution of linalool in Michelia alba.Molecules. 2010 Jul 12;15(7):4890-7. doi: 10.3390/molecules15074890. Molecules. 2010. PMID: 20657397 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge Mapping of Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels (Danggui) Research: A Scientometric Study.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Mar 13;11:294. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00294. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32231572 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic comparison of ferulic acid in normal and blood deficiency rats after oral administration of Angelica sinensis, Ligusticum chuanxiong and their combination.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(3):3583-97. doi: 10.3390/ijms13033583. Epub 2012 Mar 16. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22489169 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the phytochemistry and pharmacology of plant-derived phthalides.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 29;9(12):e22957. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22957. eCollection 2023 Dec. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38076133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative analysis of the main bioactive components of San-ao decoction and its series of formulations.Molecules. 2012 Nov 1;17(11):12925-37. doi: 10.3390/molecules171112925. Molecules. 2012. PMID: 23117432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xue T., Roy R. Studying traditional Chinese medicine. Science. 2003;300:740–741. - PubMed
-
- Tang Y.P., Duan J.A., Ding A.W., Shang E.X., Lu Y., Fan X.S. Strategy for studying the substantial basis of TCM formulae. Shijie Kexue jishu-Zhongyiyao Xiandaihua. 2007;9:20–24.
-
- Fan L., Sun J.H., Wang C.N., Qian G.Z., Feng C.H., Min Y., Cao Y.F., Wang G.Q. Effect of extract liquid of Ligusticum chuanxiong and Angelica sinensis on rat model of acute cerebral infarction. Zhongguo Linchuang Yaoxue Zazhi. 2002;11:81–83.
-
- Sun R.Z., Wang R.Q. Reperfusion injury effect of Chinese Angelica and ligustrazine on skeletal muscles of rabbit. Zhongguo Zhongyiyao Xinxi Zazhi. 2002;9:30–31.
-
- Zhang X.J., Cao Y.F., Feng C.H., Fan L., Wang C.A., Qian G.Z., Min Y., Wang G.Q. Effect of extract liquid of Ligusticum chuanxiong and Angelica sinensis on thrombosis. Zhongguo Linchuang Yaoxue Zazhi. 2002;11:45–46.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

