Luteolin isolated from the flowers of Lonicera japonica suppresses inflammatory mediator release by blocking NF-kappaB and MAPKs activation pathways in HMC-1 cells
- PMID: 20110898
- PMCID: PMC6257122
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules15010385
Luteolin isolated from the flowers of Lonicera japonica suppresses inflammatory mediator release by blocking NF-kappaB and MAPKs activation pathways in HMC-1 cells
Abstract
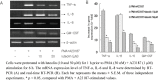
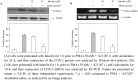
Luteolin (3',4',5,7-tetrahydroxylflavone) is a plant flavonoid and pharmacologically active agent that has been isolated from several plant species. In the present study, the effect of luteolin from the flowers of Lonicera japonica on phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) plus A23187-induced mast cell activation was examined. Luteolin significantly inhibited the induction of inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)-8, IL-6 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) by PMA plus A23187. Moreover, luteolin attenuated cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 expression and intracellular Ca2+ levels. In activated HMC-1 cells, the phosphorylation of extra-signal response kinase (ERK 1/2) and c-jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK 1/2), but not p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) were decreased by treatment of the cells with luteolin. Luteolin inhibited PMA plus A23187-induced nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB activation, IkappaB degradation, and luciferase activity. Furthermore, luteolin suppressed the expression of TNF-alpha, IL-8, IL-6, GM-CSF, and COX-2 through a decrease in the intracellular Ca2+ levels, and also showed a suppression of the ERK 1/2, JNK 1/2, and NF-kappaB activation. These results indicated that luteolin from the flowers of Lonicera japonica exerted a regulatory effect on mast cell-mediated inflammatory diseases, such as RA, allergy disease and IBD.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of resveratrol in activated HMC-1 cells: pivotal roles of NF-kappaB and MAPK.Pharmacol Res. 2009 May;59(5):330-7. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2009.01.009. Epub 2009 Jan 29. Pharmacol Res. 2009. PMID: 19416633
-
Apigenin inhibits release of inflammatory mediators by blocking the NF-κB activation pathways in the HMC-1 cells.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2011 Sep;33(3):473-9. doi: 10.3109/08923973.2010.538851. Epub 2010 Dec 13. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2011. PMID: 21142820
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of salidroside on phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate plus A23187-mediated inflammation in HMC-1 cells.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Dec;38(6):1864-1870. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2781. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27779653
-
Protective effect of luteolin against chemical and natural toxicants by targeting NF-κB pathway.Biofactors. 2022 Jul;48(4):744-762. doi: 10.1002/biof.1876. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Biofactors. 2022. PMID: 35861671 Review.
-
Powerful anti-inflammatory action of luteolin: Potential increase with IL-38.Biofactors. 2021 Mar;47(2):165-169. doi: 10.1002/biof.1718. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Biofactors. 2021. PMID: 33755250 Review.
Cited by
-
Dietary flavones counteract phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-induced SREBP-2 processing in hepatic cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2017 Jan;424(1-2):163-172. doi: 10.1007/s11010-016-2851-6. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Mol Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 27778136
-
Systems pharmacology uncovers Janus functions of botanical drugs: activation of host defense system and inhibition of influenza virus replication.Integr Biol (Camb). 2013 Feb;5(2):351-71. doi: 10.1039/c2ib20204b. Integr Biol (Camb). 2013. PMID: 23168537 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Neuroinflammatory Potential of Natural Products in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Molecules. 2023 Feb 3;28(3):1486. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031486. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36771152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Application of Lonicera japonica Extracts in Animal Production: From the Perspective of Intestinal Health.Front Microbiol. 2021 Aug 9;12:719877. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.719877. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34434181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fighting cytokine storm and immunomodulatory deficiency: By using natural products therapy up to now.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 12;14:1111329. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1111329. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37124230 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhu Z., Homer R.J., Wang Z., Chen Q., Geba G.P., Wang J., Zhang Y., Elias J.A. Pulmonary expression of interleukin-13 causes inflammation, mucus hypersecretion, subepithelial fibrosis, physiologic abnormalities, and eotaxin production. J. Clin. Invest. 1999;103:779–788. doi: 10.1172/JCI5909. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stassen M., Müller C., Arnold M., Hültner L., Klein-Hessling S., Neudörfl C., Reineke T., Serfling E., Schmitt E. IL-9 and IL-13 production by activated mast cells is strongly enhanced in the presence of lipopolysaccharide: NF-kappa B is decisively involved in the expression of IL-9. J. Immunol. 2000;166:4391–4398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

