Cell mechanics and the cytoskeleton
- PMID: 20110992
- PMCID: PMC2851742
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08908
Cell mechanics and the cytoskeleton
Abstract
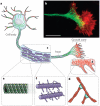
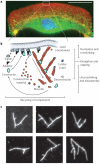
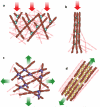
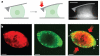
The ability of a eukaryotic cell to resist deformation, to transport intracellular cargo and to change shape during movement depends on the cytoskeleton, an interconnected network of filamentous polymers and regulatory proteins. Recent work has demonstrated that both internal and external physical forces can act through the cytoskeleton to affect local mechanical properties and cellular behaviour. Attention is now focused on how cytoskeletal networks generate, transmit and respond to mechanical signals over both short and long timescales. An important insight emerging from this work is that long-lived cytoskeletal structures may act as epigenetic determinants of cell shape, function and fate.
Figures
References
-
- Weiss PA. In: The Molecular Control of Cellular Activity. Allen JM, editor. McGraw-Hill; 1961. pp. 1–72.
-
- dos Remedios CG, et al. Actin binding proteins: regulation of cytoskeletal microfilaments. Physiol. Rev. 2003;83:433–473. - PubMed
-
- Bieling P, et al. Reconstitution of a microtubule plus-end tracking system in vitro. Nature. 2007;450:1100–1105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

