Crosstalk between C/EBPbeta phosphorylation, arginine methylation, and SWI/SNF/Mediator implies an indexing transcription factor code
- PMID: 20111005
- PMCID: PMC2845275
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.3
Crosstalk between C/EBPbeta phosphorylation, arginine methylation, and SWI/SNF/Mediator implies an indexing transcription factor code
Abstract
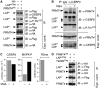
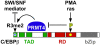
Cellular signalling cascades regulate the activity of transcription factors that convert extracellular information into gene regulation. C/EBPbeta is a ras/MAPkinase signal-sensitive transcription factor that regulates genes involved in metabolism, proliferation, differentiation, immunity, senescence, and tumourigenesis. The protein arginine methyltransferase 4 PRMT4/CARM1 interacts with C/EBPbeta and dimethylates a conserved arginine residue (R3) in the C/EBPbeta N-terminal transactivation domain, as identified by mass spectrometry of cell-derived C/EBPbeta. Phosphorylation of the C/EBPbeta regulatory domain by ras/MAPkinase signalling abrogates the interaction between C/EBPbeta and PRMT4/CARM1. Differential proteomic screening, protein interaction studies, and mutational analysis revealed that methylation of R3 constraines interaction with SWI/SNF and Mediator complexes. Mutation of the R3 methylation site alters endogenous myeloid gene expression and adipogenic differentiation. Thus, phosphorylation of the transcription factor C/EBPbeta couples ras signalling to arginine methylation and regulates the interaction of C/EBPbeta with epigenetic gene regulatory protein complexes during cell differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Baer M, Johnson PF (2000) Generation of truncated C/EBPbeta isoforms by in vitro proteolysis. J Biol Chem 275: 26582–26590 - PubMed
-
- Bartel RL, Borchardt RT (1984) Effects of adenosine dialdehyde on S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase and S-adenosylmethionine-dependent transmethylations in mouse L929 cells. Mol Pharmacol 25: 418–424 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

