Development of resistance to dasatinib in Bcr/Abl-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 20111071
- PMCID: PMC3038787
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2009.302
Development of resistance to dasatinib in Bcr/Abl-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
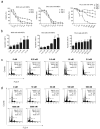
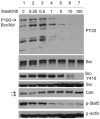
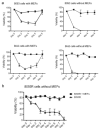
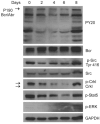
Dasatinib is a potent dual Abl/Src inhibitor approved for treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph-positive) leukemias. At a once-daily dose and a relatively short half-life of 3-5 h, tyrosine kinase inhibition is not sustained. However, transient inhibition of K562 leukemia cells with a high-dose pulse of dasatinib or long-term treatment with a lower dose was reported to irreversibly induce apoptosis. Here, the effect of dasatinib on treatment of Bcr/Abl-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cells was evaluated in the presence of stromal support. Dasatinib eradicated Bcr/Abl ALL cells, caused significant apoptosis and eliminated tyrosine phosphorylation on Bcr/Abl, Src, Crkl and Stat-5. However, treatment of mouse ALL cells with lower doses of dasatinib over an extended period of time allowed the emergence of viable drug-resistant cells. Interestingly, dasatinib treatment increased cell-surface expression of CXCR4, which is important for survival of B-lineage cells, but this did not promote survival. Combined treatment of cells with dasatinib and a CXCR4 inhibitor resulted in enhanced cell death. These results do not support the concept that long-term treatment with low-dose dasatinib monotherapy will be effective in causing irreversible apoptosis in Ph-positive ALL, but suggest that combined treatment with dasatinib and drugs such as AMD3100 may be effective.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activity of the Aurora kinase inhibitor VX-680 against Bcr/Abl-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemias.Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 May;9(5):1318-27. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0069. Epub 2010 Apr 13. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010. PMID: 20388735 Free PMC article.
-
Cotreatment with vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid) enhances activity of dasatinib (BMS-354825) against imatinib mesylate-sensitive or imatinib mesylate-resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Oct 1;12(19):5869-78. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0980. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17020995
-
Effects of dasatinib on SRC kinase activity and downstream intracellular signaling in primitive chronic myelogenous leukemia hematopoietic cells.Cancer Res. 2008 Dec 1;68(23):9624-33. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1131. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 19047139 Free PMC article.
-
Dasatinib: a tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia and philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Clin Ther. 2007 Nov;29(11):2289-308. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.11.005. Clin Ther. 2007. PMID: 18158072 Review.
-
[Pharmacological properties and clinical efficacy of dasatinib hydrate (Sprycel), an anticancer drug for chronic myelogenous leukemia and Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2009 Sep;134(3):159-67. doi: 10.1254/fpj.134.159. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2009. PMID: 19749489 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia and stromal cells communicate through Galectin-3.Oncotarget. 2015 May 10;6(13):11378-94. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3409. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25869099 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Analyses of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Ph+ and Ph-Like-Recent Progress in Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 15;22(12):6411. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126411. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34203891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effector-mediated eradication of precursor B acute lymphoblastic leukemia with a novel Fc-engineered monoclonal antibody targeting the BAFF-R.Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 Jun;13(6):1567-77. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-1023. Epub 2014 May 13. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014. PMID: 24825858 Free PMC article.
-
The MitoNEET Ligand NL-1 Mediates Antileukemic Activity in Drug-Resistant B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2019 Jul;370(1):25-34. doi: 10.1124/jpet.118.255984. Epub 2019 Apr 22. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2019. PMID: 31010844 Free PMC article.
-
Leukaemia: a model metastatic disease.Nat Rev Cancer. 2021 Jul;21(7):461-475. doi: 10.1038/s41568-021-00355-z. Epub 2021 May 5. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33953370 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Faderl S, Garcia-Manero G, Thomas DA, Kantarjian HM. Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia- current concepts and future perspectives. Rev Clin Exp Hematol. 2002;6:142–160. - PubMed
-
- Ren R. Mechanisms of BCR-ABL in the pathogenesis of chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:172–183. - PubMed
-
- Danhauser-Riedl S, Warmuth M, Druker BJ, Emmerich B, Hallek M. Activation of Src kinases p53/56lyn and p59hck by p210bcr/abl in myeloid cells. Cancer Res. 1996;56:3589–3596. - PubMed
-
- Lionberger JM, Wilson MB, Smithgall TE. Transformation of myeloid leukemia cells to cytokine independence by Bcr-Abl is suppressed by kinase-defective Hck. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:18581–18585. - PubMed

