The relation between myocardial blush grade and myocardial contrast echocardiography: which one is a better predictor of myocardial damage?
- PMID: 20111640
- PMCID: PMC2810032
The relation between myocardial blush grade and myocardial contrast echocardiography: which one is a better predictor of myocardial damage?
Abstract
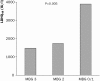
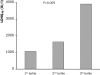
Background. Myocardial blush grade (MBG) and myocardial contrast echocardiography (MCE) are both indices for myocardial perfusion in patients with ST-elevation acute myocardial infarction (STEMI). We aimed to compare MBG with MCE in the infarct-related artery segment for assessing infarct size in patients with STEMI treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).Methods. 43 patients underwent successful (postprocedural TIMI flow 3) primary PCI for STEMI. MBG was assessed at the end of the PCI procedure and MCE was assessed 1.7+/-1.8 days after PCI. Enzymatic infarct size was estimated by measurementof enzyme activities by using lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) as the referenceenzyme. Cumulative enzyme release (LDHQ(48)) from at least five serial measurements up to 48 hours after symptom onset was calculated. Also peak creatine kinase, CK-MB and peak LDH were measured.Results. MBG 0/1, 2 and 3 were observed in 14, 12 and 17 patients, respectively, and was compared with tertiles of MCE. We found a parallel correlation between both MBG and MCE and LDHQ(48). However, there was no correlation between MCE and MBG. Patients with both normal MCE and a normal MBG had least myocardial damage and those with both impaired MCE and an impaired MBG had most myocardial damage.Conclusion. Both MBG and MCE are good predictors of infarct size in STEMI patients treated with PCI. However, these markers are not mutually related, possibly due to time-related changes in myocardial perfusion. Combining these two markers may yield a more accurate prediction of final myocardial damage. (Neth Heart J 2010;18:25-30.).
Keywords: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; infarct size; myocardial blush grade; myocardial contrast echocardiography.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mean platelet volume is associated with poor postinterventional myocardial blush grade in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.Coron Artery Dis. 2013 Jun;24(4):285-9. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0b013e328360eff6. Coron Artery Dis. 2013. PMID: 23542159
-
Effect of high-intensity statin preloading on TIMI flow in patients presenting with ST-elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention.Egypt Heart J. 2020 Jul 10;72(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s43044-020-00074-0. Egypt Heart J. 2020. PMID: 32651772 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of myocardial blush grade on Tpe interval and Tpe/QT ratio after successful primary percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with ST elevation myocardial infarction.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017 Jan;21(1):143-149. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28121344
-
Remote ischemic post-conditioning of the lower limb during primary percutaneous coronary intervention safely reduces enzymatic infarct size in anterior myocardial infarction: a randomized controlled trial.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013 Oct;6(10):1055-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2013.05.011. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013. PMID: 24156966 Clinical Trial.
-
The central role of conventional 12-lead ECG for the assessment of microvascular obstruction after percutaneous myocardial revascularization.J Electrocardiol. 2014 Jan-Feb;47(1):45-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2013.10.002. Epub 2013 Oct 17. J Electrocardiol. 2014. PMID: 24290322 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative myocardial blush score (QuBE) allows the prediction of heart failure development in long-term follow-up in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: Proof of concept study.Cardiol J. 2019;26(4):322-332. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2017.0129. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Cardiol J. 2019. PMID: 29131283 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of Myocardial Blush Grade in ST-elevation MI: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Interv Cardiol. 2022 Jul 21;17:e10. doi: 10.15420/icr.2022.01. eCollection 2022 Jan. Interv Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35923767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low Quantitative Blush Evaluator score predicts larger infarct size and reduced left ventricular systolic function in patients with STEMI regardless of diabetes status.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 5;13(1):250. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-24855-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36604458 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of collaterals on deaths and re-infarctions in patients with coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis.Neth Heart J. 2013 Mar;21(3):146-51. doi: 10.1007/s12471-012-0361-z. Neth Heart J. 2013. PMID: 23208154 Free PMC article.
-
CHA2DS2-VASc Score as an Independent Predictor of Suboptimal Reperfusion and Short-Term Mortality after Primary PCI in Patients with Acute ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Feb 1;55(2):35. doi: 10.3390/medicina55020035. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 30717292 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bowers TR, O'Neill WW. Beyond TIMI III flow. Circulation. 2000;101:2332–4. - PubMed
-
- Henriques JP, Zijlstra F, Ottervanger JP, de Boer MJ, van 't Hof AWJ, Hoorntje JCA, et al. Incidence and clinical significance of distal embolization during primary angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2002:23:1112–7. - PubMed
-
- Haager PK, Christott P, Heussen N, Lepper W, Hanrath P, Hoffmann R. Prediction of clinical outcome after mechanical revascularization in acute myocardial infarction by markers of myocardial reperfusion. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003:41:532–8. - PubMed
-
- Van 't Hof AWJ, Liem A, Suryapranata H, Hoorntje JCA, de Boer MJ, Zijlstra F, on behalf of the Zwolle Myocardial Infarction Study Group. Angiographic assessment of myocardial reperfusion in patients treated with primary angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1998;97:2302–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
