Activation-induced T helper cell death contributes to Th1/Th2 polarization following murine Schistosoma japonicum infection
- PMID: 20111738
- PMCID: PMC2810471
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/202397
Activation-induced T helper cell death contributes to Th1/Th2 polarization following murine Schistosoma japonicum infection
Abstract
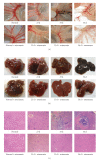
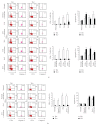
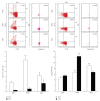
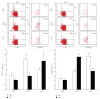
In chronic infectious diseases, such as schistosomiasis, pathogen growth and immunopathology are affected by the induction of a proper balanced Th1/Th2 response to the pathogen and by antigen-triggered activation-induced T cell death. Here, by using S. japonicum infection or schistosome antigens-immunized mouse model, or antigens in vitro stimulation, we report that during the early stage of S. japonicum infection, nonegg antigens trigger Th2 cell apoptosis via the granzyme B signal pathway, contributing to Th1 polarization, which is thought to be associated with worm clearance and severe schistosomiasis. Meanwhile, after the adult worms lay their eggs, the egg antigens trigger Th1 cell apoptosis via the caspase pathway, contributing to Th2 polarization, which is associated with mild pathology and enhanced survival of both worms and their hosts. Thus, our study suggests that S. japonicum antigen-induced Th1 and Th2 cell apoptosis involves the Th1/Th2 shift and favorites both hosts and parasites.
Figures


References
-
- Infante-Duarte C. Th1/Th2 balance in infection. Springer Seminars in Immunopathology. 1999;21(3):317–338. - PubMed
-
- Rogers PR, Croft M. Peptide dose, affinity, and time of differentiation can contribute to the Th1/Th2 cytokine balance. Journal of Immunology. 1999;163(3):1205–1213. - PubMed
-
- Balkhi MY, Latchumanan VK, Singh B, Sharma P, Natarajan K. Cross-regulation of CD86 by CD80 differentially regulates T helper responses from Mycobacterium tuberculosis secretory antigen-activated dendritic cell subsets. Journal of Leukocyte Biology. 2004;75(5):874–883. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

