The unexpected role for the aryl hydrocarbon receptor on susceptibility to experimental toxoplasmosis
- PMID: 20111744
- PMCID: PMC2810477
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/505694
The unexpected role for the aryl hydrocarbon receptor on susceptibility to experimental toxoplasmosis
Abstract
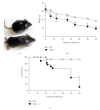
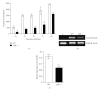
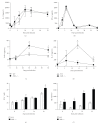
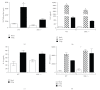
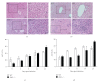
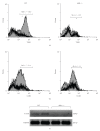
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is part of a signaling system that is mainly triggered by xenobiotic agents. Increasing evidence suggests that AhR may regulate immunity to infections. To determine the role of AhR in the outcome of toxoplasmosis, we used AhR-/- and wild-type (WT) mice. Following an intraperitoneal infection with Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii), AhR-/- mice succumbed significantly faster than WT mice and displayed greater liver damage as well as higher serum levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, nitric oxide (NO), and IgE but lower IL-10 secretion. Interestingly, lower numbers of cysts were found in their brains. Increased mortality was associated with reduced expression of GATA-3, IL-10, and 5-LOX mRNA in spleen cells but higher expression of IFN-gamma mRNA. Additionally, peritoneal exudate cells from AhR-/- mice produced higher levels of IL-12 and IFN-gamma but lower TLR2 expression than WT mice. These findings suggest a role for AhR in limiting the inflammatory response during toxoplasmosis.
Figures
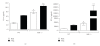

References
-
- Whitlock JP., Jr. Induction of cytochrome P4501A1. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology. 1999;39:103–125. - PubMed
-
- Denison MS, Nagy SR. Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor by structurally diverse exogenous and endogenous chemicals. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology. 2003;43:309–334. - PubMed
-
- Lai Z-W, Hundeiker C, Gleichmann E, Esser C. Cytokine gene expression during ontogeny in murine thymus on activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Molecular Pharmacology. 1997;52(1):30–37. - PubMed
-
- N'Diaye M, Le Ferrec E, Lagadic-Gossmann D, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor- and calcium-dependent induction of the chemokine CCL1 by the environmental contaminant benzo[a]pyrene. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2006;281(29):19906–19915. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

