New biotechnological and nanomedicine strategies for treatment of lysosomal storage disorders
- PMID: 20112244
- PMCID: PMC4002210
- DOI: 10.1002/wnan.73
New biotechnological and nanomedicine strategies for treatment of lysosomal storage disorders
Abstract
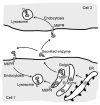
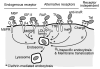
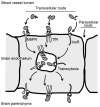
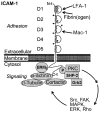
This review discusses the multiple bio- and nanotechnological strategies developed in the last few decades for treatment of a group of fatal genetic diseases termed lysosomal storage disorders. Some basic foundation on the biomedical causes and social and clinical relevance of these diseases is provided. Several treatment modalities, from those currently available to novel therapeutic approaches under development, are also discussed; these include gene and cell therapies, substrate reduction therapy, chemical chaperones, enzyme replacement therapy, multifunctional chimeras, targeting strategies, and drug carrier approaches.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Treatment strategies for lysosomal storage disorders.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2018 Jan;60(1):13-18. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.13600. Epub 2017 Nov 1. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29090451 Review.
-
Lysosomal storage diseases: from pathophysiology to therapy.Annu Rev Med. 2015;66:471-86. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-122313-085916. Annu Rev Med. 2015. PMID: 25587658 Review.
-
Enzyme replacement therapy and beyond-in memoriam Roscoe O. Brady, M.D. (1923-2016).J Inherit Metab Dis. 2017 May;40(3):343-356. doi: 10.1007/s10545-017-0032-8. Epub 2017 Mar 17. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2017. PMID: 28314976 Review.
-
New strategies for the treatment of lysosomal storage diseases (review).Int J Mol Med. 2013 Jan;31(1):11-20. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.1187. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Int J Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23165354 Review.
-
Therapeutic Approaches in Lysosomal Storage Diseases.Biomolecules. 2021 Nov 26;11(12):1775. doi: 10.3390/biom11121775. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34944420 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Flow shear stress differentially regulates endothelial uptake of nanocarriers targeted to distinct epitopes of PECAM-1.J Control Release. 2015 Jul 28;210:39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.05.006. Epub 2015 May 9. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 25966362 Free PMC article.
-
Biocompatible Polymer Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Applications in Cancer and Neurodegenerative Disorder Therapies.J Funct Biomater. 2019 Jan 8;10(1):4. doi: 10.3390/jfb10010004. J Funct Biomater. 2019. PMID: 30626094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted enzyme delivery systems in lysosomal disorders: an innovative form of therapy for mucopolysaccharidosis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Sep;76(17):3363-3381. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03135-z. Epub 2019 May 17. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31101939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticles restore lysosomal acidification defects: Implications for Parkinson and other lysosomal-related diseases.Autophagy. 2016;12(3):472-83. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1136769. Autophagy. 2016. PMID: 26761717 Free PMC article.
-
Application of advances in endocytosis and membrane trafficking to drug delivery.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;157:118-141. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.07.026. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020. PMID: 32758615 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sabatini DD, Adesnik MB. The biogenesis of membranes and organelles. In: Scriver C, Beaudet A, Sly W, Valle D, Childs B, Kinzler K, Vogelstein B, editors. Lysosomal disorders the metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2001. pp. 433–520.
-
- Scriver C, Beaudet A, Sly W, Valle D, Childs B, Kinzler K, Vogelstein B. The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. 8. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2001.
-
- Futerman AH, van Meer G. The cell biology of lysosomal storage disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:554–565. - PubMed
-
- Meikle PJ, Hopwood JJ, Clague AE, Carey WF. Prevalence of lysosomal storage disorders. Jama. 1999;281:249–254. - PubMed
-
- Schuchman EH, Desnick RJ. Niemann-Pick disease types A and B: Acid sphingomyelinase deficiencies. In: Scriver C, Beaudet A, Sly W, Valle D, Childs B, Kinzler K, Vogelstein B, editors. Lysosomal disorders the metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2001. pp. 3589–3610.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

