Genotoxicity of pyrrolizidine alkaloids
- PMID: 20112250
- PMCID: PMC6376482
- DOI: 10.1002/jat.1504
Genotoxicity of pyrrolizidine alkaloids
Abstract
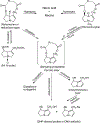
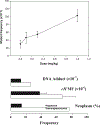
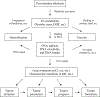
Pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) are common constituents of many plant species around the world. PA-containing plants are probably the most common poisonous plants affecting livestock and wildlife. They can inflict harm to humans through contaminated food sources, herbal medicines and dietary supplements. Half of the identified PAs are genotoxic and many of them are tumorigenic. The mutagenicity of PAs has been extensively studied in different biological systems. Upon metabolic activation, PAs produce DNA adducts, DNA cross-linking, DNA breaks, sister chromatid exchange, micronuclei, chromosomal aberrations, gene mutations and chromosome mutations in vivo and in vitro. PAs induced mutations in the cII gene of rat liver and in the p53 and K-ras genes of mouse liver tumors. It has been suggested that all PAs produce a set of (+/-)-6,7-dihydro-7-hydroxy-1-hydroxymethyl-5H-pyrrolizine-derived DNA adducts and similar types of gene mutations. The signature types of mutations are G : C --> T : A transversion and tandem base substitutions. Overall, PAs are mutagenic in vivo and in vitro and their mutagenicity appears to be responsible for the carcinogenesis of PAs.
(c) 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Allen JR, Hsu IC, Carstens LA. 1975. Dehydroretronecine-induced rhabdomyosarcomas in rats. Cancer Res. 35: 997–1002. - PubMed
-
- Arseculeratne SN, Gunatilaka AA, Panabokke RG. 1981. Studies on medicinal plants of Sri Lanka: occurrence of pyrrolizidine alkaloids and hepatotoxic properties in some traditional medicinal herbs. J. Ethnopharmacol 4: 159–177. - PubMed
-
- Arseculeratne SN, Gunatilaka AA, Panabokke RG. 1985. Studies of medicinal plants of Sri Lanka. Part 14: toxicity of some traditional medicinal herbs. J. Ethnopharmacol 13: 323–335. - PubMed
-
- Arzt J, Mount ME. 1999. Hepatotoxicity associated with pyrrolizidine alkaloid (Crotalaria spp) ingestion in a horse on Easter Island. Vet. Hum. Toxicol 41: 96–99. - PubMed
-
- Bach N, Thung SN, Schaff ner F. 1989. Comfrey herb tea-induced hepatic veno-occlusive disease. Am. J. Med 87: 97–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

