Histone modifications: crucial elements for damage response and chromatin restoration
- PMID: 20112283
- PMCID: PMC2930755
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.22060
Histone modifications: crucial elements for damage response and chromatin restoration
Abstract
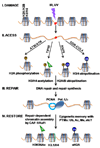
Eukaryotic genomes are packaged into chromatin from repeated nucleosome arrays in which DNA sequences wrap around histones. Chromatin organization has profound influence on DNA-templated processes such as transcription, DNA replication, and repair. Recent studies have also revealed chromatin dynamics as an active contributor to diverse DNA damage responses (DDR). Here, we review recent progress in histone modification related to DDR and post-repair chromatin restoration at the sites of DNA damage. We discuss how the timing and features of histone modifications would provide the initial as well as the final guidance for DDR, and the prospect that modifications may challenge the epigenetic stability of repaired cells and serve as damage memory in chromatin.
Figures
References
-
- Benson LJ, Gu Y, Yakovleva T, Tong K, Barrows C, Strack CL, Cook RG, Mizzen CA, Annunziato AT. Modifications of H3 and H4 during chromatin replication, nucleosome assembly, and histone exchange. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:9287–9296. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein BE, Meissner A, Lander ES. The mammalian epigenome. Cell. 2007;128:669–681. - PubMed
-
- Bird AW, Yu DY, Pray-Grant MG, Qiu Q, Harmon KE, Megee PC, Grant PA, Smith MM, Christman MF. Acetylation of histone H4 by Esa1 is required for DNA double-strand break repair. Nature. 2002;419:411–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

