Bim-Bcl-2 homology 3 mimetic therapy is effective at suppressing inflammatory arthritis through the activation of myeloid cell apoptosis
- PMID: 20112357
- PMCID: PMC2848986
- DOI: 10.1002/art.27198
Bim-Bcl-2 homology 3 mimetic therapy is effective at suppressing inflammatory arthritis through the activation of myeloid cell apoptosis
Abstract
Objective: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a destructive autoimmune disease characterized by an increased inflammation in the joint. Therapies that activate the apoptotic cascade may have potential for use in RA; however, few therapeutic agents fit this category. The purpose of this study was to examine the potential of Bim, an agent that mimics the action of Bcl-2 homology 3 (BH3) domain-only proteins that have shown success in preclinical studies of cancer, in the treatment of autoimmune disease.
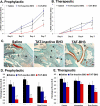
Methods: Synovial tissues from RA and osteoarthritis patients were analyzed for the expression of Bim and CD68 using immunohistochemistry. Macrophages from Bim(-/-) mice were examined for their response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) using flow cytometry, real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and immunoblotting. Bim(-/-) mice were stimulated with thioglycollate or LPS and examined for macrophage activation and cytokine production. Experimental arthritis was induced using the K/BxN serum-transfer model. A mimetic peptide corresponding to the BH3 domain of Bim (TAT-BH3) was administered as a prophylactic agent and as a therapeutic agent. Edema of the ankles and histopathologic analysis of ankle tissue sections were used to determine the severity of arthritis, its cellular composition, and the degree of apoptosis.
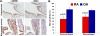
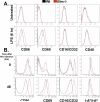
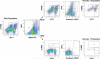
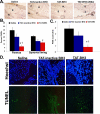
Results: The expression of Bim was reduced in RA synovial tissue as compared with controls, particularly in macrophages. Bim(-/-) macrophages displayed elevated expression of markers of inflammation and secreted more interleukin-1beta following stimulation with LPS or thioglycollate. TAT-BH3 ameliorated arthritis development, reduced the number of myeloid cells in the joint, and enhanced apoptosis without inducing cytotoxicity.
Conclusion: These data demonstrate that BH3 mimetic therapy may have significant potential for the treatment of RA.
Figures
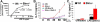
Similar articles
-
Bim deficiency leads to exacerbation and prolongation of joint inflammation in experimental arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Oct;54(10):3182-93. doi: 10.1002/art.22133. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 17009248
-
IL-10/Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling dysregulates Bim expression in autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 Mar;135(3):762-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.07.020. Epub 2014 Aug 28. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25174872 Free PMC article.
-
The BH3-only proteins Bim and Puma cooperate to impose deletional tolerance of organ-specific antigens.Immunity. 2012 Sep 21;37(3):451-62. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.05.030. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Immunity. 2012. PMID: 22960223 Free PMC article.
-
The BH3 alpha-helical mimic BH3-M6 disrupts Bcl-X(L), Bcl-2, and MCL-1 protein-protein interactions with Bax, Bak, Bad, or Bim and induces apoptosis in a Bax- and Bim-dependent manner.J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 18;286(11):9382-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.203638. Epub 2010 Dec 9. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21148306 Free PMC article.
-
BH3-only proteins in rheumatoid arthritis: potential targets for therapeutic intervention.Oncogene. 2008 Dec;27 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S168-75. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.54. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 19641502 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting RIP Kinases in Chronic Inflammatory Disease.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 28;11(5):646. doi: 10.3390/biom11050646. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33924766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defective T-Cell Apoptosis and T-Regulatory Cell Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Cells. 2018 Nov 22;7(12):223. doi: 10.3390/cells7120223. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30469466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cationic Arginine-Rich Peptides (CARPs): A Novel Class of Neuroprotective Agents With a Multimodal Mechanism of Action.Front Neurol. 2020 Feb 25;11:108. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00108. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32158425 Free PMC article.
-
Bcl-2-regulated cell death signalling in the prevention of autoimmunity.Cell Death Dis. 2010 Jun 3;1(6):e48. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2010.27. Cell Death Dis. 2010. PMID: 21364654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ApoE deficiency exacerbates the development and sustainment of a semi-chronic K/BxN serum transfer-induced arthritis model.J Transl Med. 2016 Jun 10;14(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-0912-y. J Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27287704 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu H, Pope RM. Apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis: friend or foe. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2004;30(3):603–25. x. - PubMed
-
- Strasser A. The role of BH3-only proteins in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5(3):189–200. - PubMed
-
- Letai A, Bassik MC, Walensky LD, Sorcinelli MD, Weiler S, Korsmeyer SJ. Distinct BH3 domains either sensitize or activate mitochondrial apoptosis, serving as prototype cancer therapeutics. Cancer Cell. 2002;2(3):183–92. - PubMed
-
- Certo M, Del Gaizo Moore V, Nishino M, Wei G, Korsmeyer S, Armstrong SA, et al. Mitochondria primed by death signals determine cellular addiction to antiapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Cancer Cell. 2006;9(5):351–65. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Willis SN, Wei A, Smith BJ, Fletcher JI, Hinds MG, et al. Differential targeting of prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins by their BH3-only ligands allows complementary apoptotic function. Mol Cell. 2005;17(3):393–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM044118/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR048269/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR049217/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI070555/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- GM-060472/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI067590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AR-054796/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR048267/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI-067590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA123067/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AR-050250/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI-067752/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM060472/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR054796/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR-048267/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM-044118/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI-040987/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AR-048269/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI-070555/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR047825/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR-049217/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA-123067/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM055194/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR050250/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM-055194/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI040987/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI067752/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AR-047825/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

