Exploratory laparoscopy--diagnosis method in pediatric surgery pathology
- PMID: 20112473
- PMCID: PMC5052501
Exploratory laparoscopy--diagnosis method in pediatric surgery pathology
Abstract
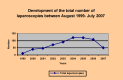
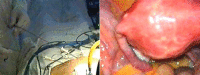
The purpose of this article is to establish the important place of laparoscopy in the diagnosis management of pediatric surgery pathology. In addition, it is intended to become a pleading, concerning the true and realistic benefit, for the pediatric patient, of minimally invasive surgery. In our country, the method was taken over from general surgery and had a few years of latency in imposing itself. We consider that each pediatric surgeon is required to have a mandatory period of training in this topic. This is the reason why we appeal to the young generations of pediatric surgeons but also to the surgeons with many years of experience in classical surgical techniques, who are able to perfect the diagnostic and treatment methods in many medical specialties. The clinical research took place in a retro and prospective manner from August 1999 to July 2007 in the Department of Pediatric Surgery "Maria Sklodowska Curie" Hospital and studied 663 laparoscopic surgeries. 83 of them were exploratory laparoscopies (39 boys and 44 girls) and the other 580 were therapeutic procedures with accurate pre-operatory diagnostics. The surgical activity of our department concerning exploratory laparoscopy was also appreciated due to the decisional and therapeutic algorithms that were conceived. The motivations for exploratory laparoscopic procedures are multiple and arise from many causes, from right lower quadrant pain syndrome and abdominal tumors to congenital malformations and non-palpable testis. The processed data revealed the utility of laparoscopy, concerning most of the pediatric surgical pathologies and in the same time allowing them to continue the exploratory method of diagnosis with a minimally invasive therapy. The discrepancy between the exploratory benefit (sometimes minor) and the surgical trauma of an open exploratory surgery, explains the utility of laparoscopy that took over most of open surgery indications.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Laparoscopic exploration in pediatric surgery emergencies.J Med Life. 2010 Jan-Mar;3(1):90-5. J Med Life. 2010. PMID: 20302204 Free PMC article.
-
Technological update of the video-endoscopic approach of the diagnosis and staging of tumors in children.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2014;55(2 Suppl):597-602. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2014. PMID: 25178331
-
[Minimally invasive surgery in pediatric patients within a general urology department].Arch Esp Urol. 2008 Jul-Aug;61(6):695-8. Arch Esp Urol. 2008. PMID: 18705190 Spanish.
-
[Laparoscopy in pediatric urology].Arch Esp Urol. 2002 Jul-Aug;55(6):737-47. Arch Esp Urol. 2002. PMID: 12224172 Review. Spanish.
-
Evolving uses of laparoscopy in children.Surg Clin North Am. 1992 Dec;72(6):1299-313. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)45882-2. Surg Clin North Am. 1992. PMID: 1440158 Review.
Cited by
-
The electromagnetic bio-field: clinical experiments and interferences.J Med Life. 2012 Jun 12;5(2):139-44. Epub 2012 Jun 18. J Med Life. 2012. PMID: 22802878 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic surgery complications: postoperative peritonitis.J Med Life. 2012 Sep 15;5(3):288-96. Epub 2012 Sep 25. J Med Life. 2012. PMID: 23049630 Free PMC article.
-
The role of laparoscopy in paediatric and adolescent gynaecology.Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2020 Sep;15(3):424-436. doi: 10.5114/wiitm.2020.97817. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2020. PMID: 32904632 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lobe E.T., Schropp K. P. Pediatric laparoscopy and thoracoscopy. Philadelphia –London-Toronto-Montreal-Sydney-Tokyo: W.B.Saunders Company; 1994. pp. 1–105.
-
- Waldschmidt J., Schier F. Laparoscopic surgery in neonates and infants. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1991;(1):145–150. - PubMed
-
- Montupet P, Esposito C. Laparoscopic herniorraphy in children. Handbook of Pediatric Laparoscopic Surgery. 2006:22.
-
- Ardela Diaz E, Diez Pascual R, Dominguez Vallejo F. J. Utilidad de la laparoscopia en la infancia. Boletin de la Sociedad de Pediatria de Asturias, Cantabria, Castilla y Leon. 2001;41(176):146.
-
- Gans S., Berci G. Peritoneoscopy in infants and children. J.Pediatr.Surg. 1973;8:399–403. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
