Bioactive lipids lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate mediate breast cancer cell biological functions through distinct mechanisms
- PMID: 20112503
- PMCID: PMC8485930
- DOI: 10.3727/096504009790217399
Bioactive lipids lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate mediate breast cancer cell biological functions through distinct mechanisms
Erratum in
- Oncol Res. 2009;18(7):357. Philippe, Clézardin [corrected to Clézardin, Philippe]; Oliver, Peyruchaud [corrected to Peyruchaud, Oliver]
Abstract
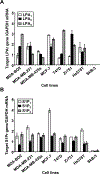
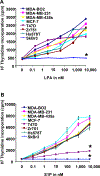
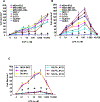
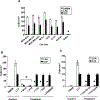
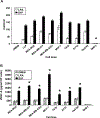
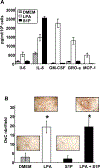
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) and sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) are structurally related bioactive lipids with growth factor-like activities. LPA and S1P are naturally produced in vivo by blood platelets upon platelet aggregation and at least in vitro by fibroblasts, adipocytes, and multiple types of tumor cells. Breast cancer cells respond to LPA and S1P. However, their specific actions on breast cancer cell biological functions remain unclear. We therefore conducted an in vitro side-by-side study of these two lipids on breast cancer cells. LPA mediates human breast cancer MDA-BO2 cell proliferation, migration, and invasion through activation of a G(alpha i)/ERK1/2-dependent signaling pathway, whereas activation of G(alpha i)/PI3K predominates upon S1P stimulation. In MDA-BO2 cells, LPA but not S1P activities were dependent on active type 1 insulin-like growth factor and epithelial growth factor receptors. LPA and S1P act directly on endothelial cells to induce angiogenesis. We demonstrate that LPA and S1P have indirect angiogenic properties as judged by induced secretion of angiogenic factors by breast cancer cells primed with these lysophospholipids. S1P, but not LPA, controlled the expression of VEGF-A by breast cancer cells, while LPA, but not S1P, controlled the expression of GM-CSF, Gro-alpha, MCP-1, and IL-6. According to the secretion of these paracrine osteoclastic factors, LPA, but not S1P, stimulates breast cancer cell-induced osteoclastogenesis. These findings suggest that, in vivo, LPA and S1P can coordinate their action on tumor and surrounding cells to induce breast cancer progression both at primary and bone metastatic sites.
Figures

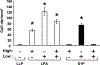

Similar articles
-
Cross-talk between LPA1 and epidermal growth factor receptors mediates up-regulation of sphingosine kinase 1 to promote gastric cancer cell motility and invasion.Cancer Res. 2008 Aug 15;68(16):6569-77. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0411. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18701480 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of endothelial cell chemotaxis by sphingosine 1-phosphate and stabilization of endothelial monolayer barrier function by lysophosphatidic acid, potential mediators of hematopoietic angiogenesis.J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 1999 Dec;8(6):627-34. doi: 10.1089/152581699319795. J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 1999. PMID: 10645770
-
Differential effects of sphingosine 1-phosphate and lysophosphatidic acid on endothelial cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 May 23;1582(1-3):190-6. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(02)00155-5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12069828 Review.
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate and lysophosphatidic acid stimulate endothelial cell migration.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000 Apr;20(4):1013-9. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.20.4.1013. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000. PMID: 10764666
-
Novel implications for lysophospholipids, lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate, as drug targets in cancer.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2009 May;9(4):381-91. doi: 10.2174/1871520610909040381. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19442039 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms linking obesity and cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1831(10):1499-508. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.02.008. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23470257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deregulated Lysophosphatidic Acid Metabolism and Signaling in Liver Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Oct 23;11(11):1626. doi: 10.3390/cancers11111626. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31652837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What Is the Role of Interleukins in Breast Cancer Bone Metastases? A Systematic Review of Preclinical and Clinical Evidence.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Dec 13;11(12):2018. doi: 10.3390/cancers11122018. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31847214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicine-Based Delivery Strategies for Breast Cancer Treatment and Management.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 5;23(5):2856. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052856. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting lysophosphatidic acid receptor type 1 with Debio 0719 inhibits spontaneous metastasis dissemination of breast cancer cells independently of cell proliferation and angiogenesis.Int J Oncol. 2012 Apr;40(4):1133-41. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2011.1309. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22200658 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
