The Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) ligand FSL-1 is internalized via the clathrin-dependent endocytic pathway triggered by CD14 and CD36 but not by TLR2
- PMID: 20113368
- PMCID: PMC2878470
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03232.x
The Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) ligand FSL-1 is internalized via the clathrin-dependent endocytic pathway triggered by CD14 and CD36 but not by TLR2
Abstract
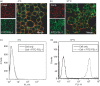
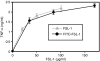
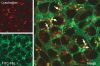
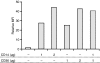
Little is known of how Toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands are processed after recognition by TLRs. This study was therefore designed to investigate how the TLR2 ligand FSL-1 is processed in macrophages after recognition by TLR2. FSL-1 was internalized into the murine macrophage cell line, RAW264.7. Both chlorpromazine and methyl-beta-cyclodextrin, which inhibit clathrin-dependent endocytosis, reduced FSL-1 uptake by RAW264.7 cells in a dose-dependent manner but nystatin, which inhibits caveolae- and lipid raft-dependent endocytosis, did not. FSL-1 was co-localized with clathrin but not with TLR2 in the cytosol of RAW264.7 cells. These results suggest that internalization of FSL-1 is clathrin dependent. In addition, FSL-1 was internalized by peritoneal macrophages from TLR2-deficient mice. FSL-1 was internalized by human embryonic kidney 293 cells transfected with CD14 or CD36 but not by the non-transfected cells. Also, knockdown of CD14 or CD36 in the transfectants reduced FSL-1 uptake. In this study, we suggest that (i) FSL-1 is internalized into macrophages via a clathrin-dependent endocytic pathway, (ii) the FSL-1 uptake by macrophages occurs irrespective of the presence of TLR2, and (iii) CD14 and CD36 are responsible for the internalization of FSL-1.
Figures







References
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov R, Janeway C., Jr Innate immunity. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:338–44. - PubMed
-
- Hallman M, Ramet M, Ezekowitz RA. Toll-like receptors as sensors of pathogens. Pediatr Res. 2001;50:315–21. - PubMed
-
- Blander JM. Signalling and phagocytosis in the orchestration of host defence. Cell Microbiol. 2007;9:290–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

