Interleukin 18 in the CNS
- PMID: 20113500
- PMCID: PMC2830964
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-9
Interleukin 18 in the CNS
Abstract
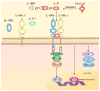
Interleukin (IL)-18 is a cytokine isolated as an important modulator of immune responses and subsequently shown to be pleiotropic. IL-18 and its receptors are expressed in the central nervous system (CNS) where they participate in neuroinflammatory/neurodegenerative processes but also influence homeostasis and behavior. Work on IL-18 null mice, the localization of the IL-18 receptor complex in neurons and the neuronal expression of decoy isoforms of the receptor subunits are beginning to reveal the complexity and the significance of the IL-18 system in the CNS. This review summarizes current knowledge on the central role of IL-18 in health and disease.
Figures
References
-
- Boraschi D, Dinarello CA. IL-18 in autoimmunity: review. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2006;17:224–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

