Detection of epithelial apoptosis in pelvic ileal pouches for ulcerative colitis and familial adenomatous polyposis
- PMID: 20113505
- PMCID: PMC2843649
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-8-11
Detection of epithelial apoptosis in pelvic ileal pouches for ulcerative colitis and familial adenomatous polyposis
Abstract
Background: Ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA) is the surgical procedure of choice for patients with refractory ulcerative colitis (UC) and for familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) with many rectal polyps. Pouchitis is one of the more frequent complications after IPAA in UC patients; however, it is rare in FAP.
Objective: Evaluate pro-apoptotic activity in endoscopically and histological normal mucosa of the ileal pouch in patients with UC and FAP.
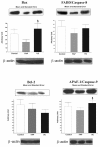
Methods: Eighteen patients (nine with UC and nine with FAP) with J pouch after total rectocolectomy were studied. Biopsies were obtained from the mucosa of the pouch and from normal ileum. The specimens were snap-frozen and the expressions of Bax and Bcl-2 were determined by immunoblot of protein extracts and by immunohistochemistry analysis. FADD, Caspase-8, APAF-1 and Caspase-9 were evaluated by immunoprecipitation and immunoblot.
Results: Patients with UC had significantly higher protein levels of Bax and APAF-1, Caspase-9 than patients with FAP, but were similar to controls. The expressions of Bcl-2 and FADD, Caspase-8 were similar in the groups. Immunohistochemistry for Bax showed less intensity of immunoreactions in FAP than in UC and Controls. Bcl-2 immunostaining was similar among the groups.
Conclusion: Patients with FAP present lower levels of pro-apoptotic proteins in all methods applied, even in the absence of clinical and endoscopic pouchitis and dysplasia in the histological analysis. These findings may explain a tendency of up-regulation of apoptosis in UC patients, resulting in higher rates of progression to pouchitis in these patients, which could correlate with mucosal atrophy that occurs in inflamed tissue. However, FAP patients had low pro-apoptotic activity in the mucosa, and it could explain the tendency to low cell turn over and presence of adenomas in this syndrome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and a pro-apoptotic protein in pelvic ileal pouches for ulcerative colitis and familial adenomatous polyposis.Tech Coloproctol. 2008 Mar;12(1):33-8. doi: 10.1007/s10151-008-0395-9. Epub 2008 May 30. Tech Coloproctol. 2008. PMID: 18512010
-
Activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription-1 (STAT-1) and differential expression of interferon-gamma and anti-inflammatory proteins in pelvic ileal pouches for ulcerative colitis and familial adenomatous polyposis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Jun;160(3):380-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.04088.x. Epub 2010 Mar 16. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20345984 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of TLR2, TLR4 and JNK in mucosa of ileal pouches for ulcerative colitis. Is there a role for bacterial antigen pathway in asymptomatic patients?Int J Clin Exp Med. 2011;4(3):179-86. Epub 2011 Sep 15. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2011. PMID: 21977230 Free PMC article.
-
Histopathological Evaluation of Pouch Neoplasia in IBD and Familial Adenomatous Polyposis.Dis Colon Rectum. 2024 Jun 1;67(S1):S91-S98. doi: 10.1097/DCR.0000000000003320. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Dis Colon Rectum. 2024. PMID: 38422398 Review.
-
Restorative proctocolectomy and ileal pouch-anal anastomosis for familial adenomatous polyposis revisited.Fam Cancer. 2006;5(3):241-60; discussion 261-2. doi: 10.1007/s10689-005-5672-4. Fam Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16998670 Review.
Cited by
-
Ileal pouch of ulcerative colitis and familial adenomatous polyposis patients exhibit modulation of autophagy markers.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 8;8(1):2619. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20938-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29422639 Free PMC article.
-
Pouchitis: insight into the pathogenesis and clinical aspects.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Jul 15;14(7):4406-4425. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35958439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ulcerative colitis with inflammatory polyposis in a teenage boy: a case report.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan 21;21(3):1044-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.1044. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25624746 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence and Risk Factors of Cancer in the Anal Transitional Zone and Ileal Pouch following Surgery for Ulcerative Colitis and Familial Adenomatous Polyposis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 21;14(3):530. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030530. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35158797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic effects of genistein in experimentally induced ulcerative colitis in rats via affecting mitochondrial biogenesis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Feb;479(2):431-444. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04746-8. Epub 2023 Apr 21. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37084167
References
-
- M'Koma AE. Serum biochemical evaluation of patients with functional pouches tem to 20 years after restorative proctocolectomy. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2006;26:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

