Statewide school-located influenza vaccination program for children 5-13 years of age, Hawaii, USA
- PMID: 20113554
- PMCID: PMC2958028
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1602.091375
Statewide school-located influenza vaccination program for children 5-13 years of age, Hawaii, USA
Abstract
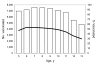
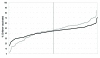
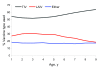
New guidance recommends annual influenza vaccination for all children 5-18 years of age in the United States. During 2007-2008, Hawaii offered inactivated and live attenuated influenza vaccine at school-located clinics for grades kindergarten through 8. Most (90%) public and private schools participated, and 622 clinics were conducted at 340 schools. Of 132,775 children 5-13 years of age, 60,760 (46%) were vaccinated. The proportion vaccinated peaked at 54% for those 6 years of age and declined for older cohorts. More than 90% of schoolchildren transited the clinic in <10 minutes. A total of 16,920 staff-hours were expended; estimated cost per dose administered was $27 and included vaccine purchase and administration, health staffing resources, printing costs, data management, and promotion. This program demonstrates the feasibility of conducting mass school-located influenza vaccination programs in public and private schools statewide, as might be indicated to respond to pandemic influenza.
Figures


References
-
- Fiore AE, Shay DK, Broder K, Iskander JK, Uyeki TM, Mootrey G, et al. Prevention and control of influenza: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2008. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2008;57(RR-7). - PubMed
-
- Davis LE, Caldwell GG, Lynch RE, Bailey RE, Chin TD. Hong Kong influenza: the epidemiologic features of a high school family study analyzed and compared with a similar study during the 1957 Asian influenza epidemic. Am J Epidemiol. 1970;92:240–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
