Catestatin: a multifunctional peptide from chromogranin A
- PMID: 20116404
- PMCID: PMC2866790
- DOI: 10.1016/j.regpep.2010.01.006
Catestatin: a multifunctional peptide from chromogranin A
Abstract
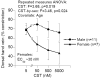
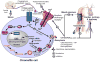
In 1997, we identified a novel peptide, catestatin (CST: bovine chromogranin A [CHGA](344-364): RSMRLSFRARGYGFRGPGLQL; human CHGA(352-372): SSMKLSFRARGYGFRGPGPQL), which is a potent inhibitor of nicotinic-cholinergic-stimulated catecholamine secretion. CST shows characteristic inhibitory effects on nicotinic cationic (Na(+), Ca(2+)) signal transduction, which are specific to the neuronal nicotinic receptor. Utilizing systematic polymorphism discovery at the human CHGA locus we discovered three human variants of CST: G(364)S, P(370)L, and R(374)Q that showed differential potencies towards the inhibition of catecholamine secretion. In humans, CHGA is elevated and its processing to CST is diminished in hypertension. Diminished CST is observed not only in hypertensive individuals but also in the early-normotensive offspring of patients with hypertension, suggesting that an early deficiency of CST might play a pathogenic role in the subsequent development of the disease. Consistent with human findings, prevention of endogenous CST expression by targeted ablation (knockout) of the mouse Chga locus (Chga-KO) resulted in severe hypertension that can be "rescued" specifically by replacement of the CST peptide. CST acts directly on the heart to inhibit the inotropic and lusitropic properties of the rodent heart and also acts as a potent vasodilator in rats and humans. While the G(364)S CST variant caused profound changes in human autonomic activity and seemed to reduce the risk of developing hypertension, CST replacement rescued Chga-KO mice from dampened baroreflex sensitivity. In addition, CST has been shown to induce chemotaxis and acts as an antimicrobial as well as an antimalarial peptide. The present review summarizes these multiple actions of CST.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
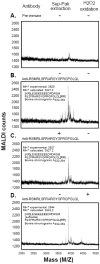
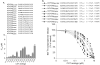
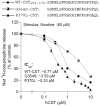

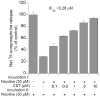


Republished in
-
Reprint of: Catestatin: a multifunctional peptide from chromogranin A.Regul Pept. 2010 Nov 30;165(1):52-62. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2010.09.007. Epub 2010 Oct 20. Regul Pept. 2010. PMID: 20965217 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taupenot L, Harper KL, O’Connor DT. Mechanisms of disease: The chromogranin-secretogranin family. New Engl J Med. 2003;348:1134–49. - PubMed
-
- Montero-Hadjadje M, Vaingankar S, Elias S, Tostivint H, Mahata SK, Anouar Y. Chromogranins A and B and secretogranin II: evolutionary and functional aspects. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2008;192:309–24. - PubMed
-
- Takiyyuddin MA, Cervenka JH, Hsiao RJ, Barbosa JA, Parmer RJ, O’Connor DT. Chromogranin A. Storage and release in hypertension. Hypertension. 1990;15:237–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

