A multi-site, two-phase, Prescription Opioid Addiction Treatment Study (POATS): rationale, design, and methodology
- PMID: 20116457
- PMCID: PMC2831115
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cct.2010.01.003
A multi-site, two-phase, Prescription Opioid Addiction Treatment Study (POATS): rationale, design, and methodology
Abstract
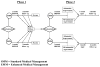
The National Institute on Drug Abuse Clinical Trials Network launched the Prescription Opioid Addiction Treatment Study (POATS) in response to rising rates of prescription opioid dependence and gaps in understanding the optimal course of treatment for this population. POATS employed a multi-site, two-phase adaptive, sequential treatment design to approximate clinical practice. The study took place at 10 community treatment programs around the United States. Participants included men and women age > or =18 who met Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, 4th Edition criteria for dependence upon prescription opioids, with physiologic features; those with a prominent history of heroin use (according to pre-specified criteria) were excluded. All participants received buprenorphine/naloxone (bup/nx). Phase 1 consisted of 4 weeks of bup/nx treatment, including a 14-day dose taper, with 8 weeks of follow-up. Phase 1 participants were monitored for treatment response during these 12 weeks. Those who relapsed to opioid use, as defined by pre-specified criteria, were invited to enter Phase 2; Phase 2 consisted of 12 weeks of bup/nx stabilization treatment, followed by a 4-week taper and 8 weeks of post-treatment follow-up. Participants were randomized at the beginning of Phase 1 to receive bup/nx, paired with either Standard Medical Management (SMM) or Enhanced Medical Management (EMM; defined as SMM plus individual drug counseling). Eligible participants entering Phase 2 were re-randomized to either EMM or SMM. POATS was developed to determine what benefit, if any, EMM offers over SMM in short-term and longer-term treatment paradigm. This paper describes the rationale and design of the study.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
References
-
- Volkow ND. Confronting the rise in abuse of prescription drugs. NIDA Notes. 2005;19(5):3.
-
- Janofsky M. Drug-Fighters Turn to Rising Tide of Prescription Abuse. The New York Times; Mar 18, 2004.
-
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. DAWN Series D-30. Rockville, MD: 2008. Drug Abuse Warning Network 2006: National Estimates of Drug-Related Emergency Department Visits.
-
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. NSDUH Series H-34. Rockville, MD: Office of Applied Studies; 2008. Results from the 2007 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: National Findings.
-
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration Office of Applied Studies. DASIS Series: S-45. National Admissions to Substance Abuse Treatment Services; Rockville, MD: 2009. Treatment Episode Data Set (TEDS). Highlights - 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous