Structure-activity relationship of new anti-tuberculosis agents derived from oxazoline and oxazole benzyl esters
- PMID: 20116900
- PMCID: PMC2843756
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2009.12.074
Structure-activity relationship of new anti-tuberculosis agents derived from oxazoline and oxazole benzyl esters
Abstract
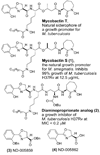
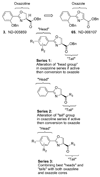
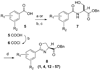
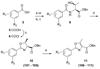
During the syntheses and studies of natural iron chelators (mycobactins), we serendipitously discovered that a simple, small molecule, oxazoline-containing intermediate 3 displayed surprising anti-tuberculosis activity (MIC of 7.7 microM, average). Herein we report elaboration of SAR around this hit as well as the syntheses and evaluation of a hundred oxazoline- and oxazole-containing compounds derived from an efficient three step process: 1) formation of beta-hydroxy amides with serine or threonine; 2) cyclization to afford oxazolines; and 3) dehydration to give the corresponding oxazoles. A number of compounds prepared by this method were shown to possess impressive activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, extremely low toxicity and therefore high therapeutic indexes, as well as activity against even the more recalcitrant non-replicating form of M. tuberculosis. The uniqueness of their structures and their simplicity should allow them to be further optimized to meet ADME (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion) requirements. The syntheses of eight of the most potent in vitro compounds were scaled up and the compounds were tested in an in vivo mouse infection model to evaluate their efficacy before engaging upon more elaborate compound design and optimization.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures
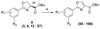
References
-
- WHO. Anti-tuberculosis Drug Resistance in the World: The WHO/IUATLD Global Project on Anti-tuberculosis Drug Resistance Surveillance 1994–1997. 1997. WHO/TB/97.229.
-
- Daniel TM, Bates JH, Downes KA. Tuberculosis: Pathogenesis, Protection, and Control, Barry Bloom editor. Washington, D.C.: ASM Press; 1994. History of Tuberculosis; pp. 13–24.
-
- WHO. Global tuberculosis control : surveillance, planning, financing : WHO report 2008. 2008. WHO/HTM/TB/2008.393.
-
- Basso LA, Blanchard JS. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1998;456:115–144. - PubMed
-
- Bradford WZ, Daley CL. Infectious Dis. Clin. North Am. 1998;12:157–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

