Functional dissection of SIRT6: identification of domains that regulate histone deacetylase activity and chromatin localization
- PMID: 20117128
- PMCID: PMC2846990
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mad.2010.01.006
Functional dissection of SIRT6: identification of domains that regulate histone deacetylase activity and chromatin localization
Abstract
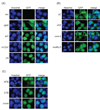
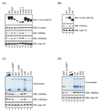
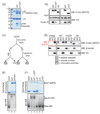
The mammalian sirtuin SIRT6 is a site-specific histone deacetylase that regulates chromatin structure. SIRT6 is implicated in fundamental biological processes in aging, including maintaining telomere integrity, fine-tuning aging-associated gene expression programs, preventing genomic instability, and maintaining metabolic homeostasis. Despite these important functions, the basic molecular determinants of SIRT6 enzymatic function--including the mechanistic and regulatory roles of specific domains of SIRT6--are not well understood. Sirtuin proteins consist of a conserved central 'sirtuin domain'--thought to comprise an enzymatic core--flanked by variable N- and C-terminal extensions. Here, we report the identification of novel functions for the N- and C-terminal domains of the human SIRT6 protein. We show that the C-terminal extension (CTE) of SIRT6 contributes to proper nuclear localization but is dispensable for enzymatic activity. In contrast, the N-terminal extension (NTE) of SIRT6 is critical for chromatin association and intrinsic catalytic activity. Surprisingly, mutation of a conserved catalytic histidine residue in the core sirtuin domain not only abrogates SIRT6 enzymatic activity but also leads to impaired chromatin association in cells. Together, our observations define important biochemical and cellular roles of specific SIRT6 domains, and provide mechanistic insight into the potential role of these domains as targets for physiologic and pharmacologic modulation.
Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Denu JM. Linking chromatin function with metabolic networks: Sir2 family of NAD(+)-dependent deacetylases. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003;28:41–48. - PubMed
-
- Frye RA. Characterization of five human cDNAs with homology to the yeast SIR2 gene: Sir2-like proteins (sirtuins) metabolize NAD and may have protein ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;260:273–279. - PubMed
-
- Frye RA. Phylogenetic classification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic Sir2-like proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;273:793–798. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

