The metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins revisited: new players, new insight
- PMID: 20117784
- PMCID: PMC3924774
- DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2009.12.027
The metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins revisited: new players, new insight
Abstract
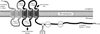
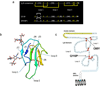
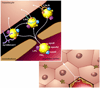
Peripheral lipoprotein lipase (LPL)-mediated lipolysis of triglycerides is the first step in chylomicron/VLDL clearance involving heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) displayed at the cell surface of the capillaries in adipose tissue, heart and skeletal muscle. The newly generated chylomicron remnant particles are then cleared by the liver, whereas VLDL remnant particles are either further modified, through the action of hepatic lipase (HL) and cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP), into LDL particles or alternatively directly cleared by the liver. Two proteins, lipase maturation factor 1 (LMF1) and glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high density lipoprotein binding protein 1 (GPIHBP1), have been recently identified and have revised our current understanding of LPL maturation and LPL-mediated lipolysis. Moreover, new insights have been gained with respect to hepatic remnant clearance using genetically modified mice targeting the sulfation of HSPGs and even deletion of the most abundant heparan sulfate proteoglycan: syndecan1. In this review, we will provide an overview of novel data on both peripheral TG hydrolysis and hepatic remnant clearance that will improve our knowledge of plasma triglyceride metabolism.
Copyright (c) 2009 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Nordestgaard BG, Benn M, Schnohr P, Tybjaerg-Hansen A. Nonfasting triglycerides and risk of myocaridal infarction, ischemic heart disease, and death in men and women. J. Am. Med. Ass. 2007;298:299–308. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg IJ, Merkel M. Lipoprotein lipase: physiology, biochemistry, and molecular biology. Front Biosci. 2001;6:D388–D405. - PubMed
-
- Bensadoun A. Lipoprotein lipase. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1991;11:217–237. - PubMed
-
- Olivecrona T, Bengtsson-Olivecrona G. Lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 1993;4:187–196.
-
- Wang H, Eckel RH. Lipoprotein Lipase: from gene to obesity. Am. J. Physiol Endocrinol. Metab. 2009;297:E271–E288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

