The executable pathway to biological networks
- PMID: 20118126
- PMCID: PMC3097101
- DOI: 10.1093/bfgp/elp054
The executable pathway to biological networks
Abstract
As time goes by, it becomes more and more apparent that the puzzles of life involve more and more molecular pieces that fit together in increasingly complex ways. Genomics and Proteomics technologies nowadays, produce reliable and quantitative data that could potentially reveal all the molecular pieces of a particular puzzle. However, this is akin to the opening of Pandora's box; and we are now facing the problem of integrating this vast amount of data with its incredible complexity into some coherent whole. With the aid of engineering methods designed to build and analyze computerized man-made systems, a new emerging field called 'Executable Biology' aims to create computer programmes that put together the pieces in ways that allows capturing their dynamicity and ultimately elucidating how molecular function generates cellular function. This review aspires to highlight the main features characterizing these kinds of executable models and what makes them uniquely qualified to reason about and analyze biological networks.
Figures
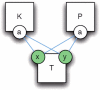




Similar articles
-
Characterizing regulatory path motifs in integrated networks using perturbational data.Genome Biol. 2010;11(3):R32. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-3-r32. Epub 2010 Mar 11. Genome Biol. 2010. PMID: 20230615 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging modeling approaches: reaction networks and rules.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;736:517-30. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-7210-1_30. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22161349 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial molecular networks: bridging the gap between functional genomics and dynamical modelling.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;804:1-11. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-361-5_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22144145 Review.
-
Detecting hierarchical modularity in biological networks.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;541:145-60. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-243-4_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19381526 Review.
-
Biological Network Inference and analysis using SEBINI and CABIN.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;541:551-76. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-243-4_24. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19381531 Review.
Cited by
-
Systems immunology: a survey of modeling formalisms, applications and simulation tools.Immunol Res. 2012 Sep;53(1-3):251-65. doi: 10.1007/s12026-012-8305-7. Immunol Res. 2012. PMID: 22528121 Review.
-
Computational Modeling, Formal Analysis, and Tools for Systems Biology.PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 Jan 21;12(1):e1004591. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004591. eCollection 2016 Jan. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016. PMID: 26795950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of proteosome-mediated proteolysis in modulating potentially harmful transcription factor activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Bioinformatics. 2011 Jul 1;27(13):i283-7. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr211. Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21685082 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the retinoid-induced differentiation of F9 embryonal stem cells by integrative genomics.Mol Syst Biol. 2011 Oct 11;7:538. doi: 10.1038/msb.2011.73. Mol Syst Biol. 2011. PMID: 21988834 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic target discovery using Boolean network attractors: improvements of kali.R Soc Open Sci. 2018 Feb 14;5(2):171852. doi: 10.1098/rsos.171852. eCollection 2018 Feb. R Soc Open Sci. 2018. PMID: 29515890 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fisher J, Henzinger TA. Executable cell biology. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:1239–49. - PubMed
-
- Regev A, Silverman W, Shapiro E. Representation and simulation of biochemical processes using the pi-calculus process algebra. Pac Symp Biocomput. 2001;6:459–70. - PubMed
-
- Priami C, Regev A, Shapiro EY, et al. Application of stochastic name-passing calculus to representation and simulation of molecular processes. Inform Proc Lett. 2001;80:25–31.
-
- Regev A, Panina EM, Silverman W, et al. Bioambients: an abstraction for biological compartments. Theoret Comput Sci. 2004;325:141–67.
-
- Kam N, Harel D, Cohen IR. Visual Languages and Formal Methods. IEEE; 2001. The immune system as a reactive system: modeling T cell activation with statecharts; pp. 15–22.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

