Gene delivery of cytochrome p450 epoxygenase ameliorates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary artery hypertension in rats
- PMID: 20118222
- PMCID: PMC2993093
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0161OC
Gene delivery of cytochrome p450 epoxygenase ameliorates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary artery hypertension in rats
Abstract
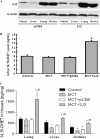
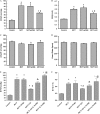
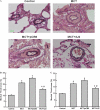
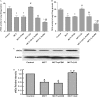
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a life-threatening disease that leads to progressive pulmonary hypertension, right heart failure, and death. Endothelial dysfunction and inflammation were implicated in the pathogenesis of PAH. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), products of the cytochrome P450 epoxygenase metabolism of arachidonic acid, are potent vasodilators that possess anti-inflammatory and other protective properties in endothelial cells. We investigated whether gene delivery with the human cytochrome P450 epoxygenase 2J2 (CYP2J2) ameliorates monocrotaline (MCT)-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Significant pulmonary hypertension developed 3 weeks after the administration of MCT, but gene therapy with CYP2J2 significantly attenuated the development of pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular remodeling, without causing changes in systemic arterial pressure or heart rate. These effects were associated with increased pulmonary endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) expression and its activity, inhibition of inflammation in the lungs, and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β/type II bone morphogenetic protein receptor (BMPRII)-drosophila mothers against decapentaplegic proteins (Smads) signaling. Collectively, these data suggest that gene therapy with CYP2J2 may have potential as a novel therapeutic approach to this progressive and oftentimes lethal disorder.
Figures
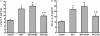


References
-
- Newman JH, Fanburg BL, Archer SL, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Garcia JG, Kao PN, Knowles JA, Loyd JE, McGoon MD, et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension: future directions: report of a National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute/Office of Rare Diseases workshop. Circulation 2004;109:2947–2952. - PubMed
-
- Itoh T, Nagaya N, Murakami S, Fujii T, Iwase T, Ishibashi-Ueda H, Yutani C, Yamagishi M, Kimura H, Kangawa K. C-type natriuretic peptide ameliorates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004;170:1204–1211. - PubMed
-
- Budhiraja R, Tuder RM, Hassoun PM. Endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 2004;109:159–165. - PubMed
-
- Ito T, Okada T, Miyashita H, Nomoto T, Nonaka-Sarukawa M, Uchibori R, Maeda Y, Urabe M, Mizukami H, Kume A, et al. Interleukin-10 expression mediated by an adeno-associated virus vector prevents monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats. Circ Res 2007;101:734–741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

