The pneumococcal cell envelope stress-sensing system LiaFSR is activated by murein hydrolases and lipid II-interacting antibiotics
- PMID: 20118250
- PMCID: PMC2838051
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01489-09
The pneumococcal cell envelope stress-sensing system LiaFSR is activated by murein hydrolases and lipid II-interacting antibiotics
Abstract
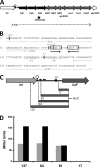
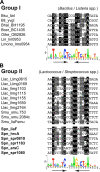
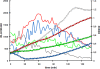
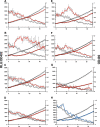
In the Firmicutes, two-component regulatory systems of the LiaSR type sense and orchestrate the response to various agents that perturb cell envelope functions, in particular lipid II cycle inhibitors. In the current study, we found that the corresponding system in Streptococcus pneumoniae displays similar properties but, in addition, responds to cell envelope stress elicited by murein hydrolases. During competence for genetic transformation, pneumococci attack and lyse noncompetent siblings present in the same environment. This phenomenon, termed fratricide, increases the efficiency of horizontal gene transfer in vitro and is believed to stimulate gene exchange also under natural conditions. Lysis of noncompetent target cells is mediated by the putative murein hydrolase CbpD, the key effector of the fratricide mechanism, and the autolysins LytA and LytC. To avoid succumbing to their own lysins, competent attacker cells must possess a protective mechanism rendering them immune. The most important component of this mechanism is ComM, an integral membrane protein of unknown function that is expressed only in competent cells. Here, we show that a second layer of self-protection is provided by the pneumococcal LiaFSR system, which senses the damage inflicted to the cell wall by CbpD, LytA, and LytC. Two members of the LiaFSR regulon, spr0810 and PcpC (spr0351), were shown to contribute to the LiaFSR-coordinated protection against fratricide-induced self-lysis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fratricide in Streptococcus pneumoniae: contributions and role of the cell wall hydrolases CbpD, LytA and LytC.Microbiology (Reading). 2009 Jul;155(Pt 7):2223-2234. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.026328-0. Epub 2009 Apr 23. Microbiology (Reading). 2009. PMID: 19389766
-
Fratricide is essential for efficient gene transfer between pneumococci in biofilms.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Aug;78(16):5897-905. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01343-12. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22706053 Free PMC article.
-
LytF, a novel competence-regulated murein hydrolase in the genus Streptococcus.J Bacteriol. 2012 Feb;194(3):627-35. doi: 10.1128/JB.06273-11. Epub 2011 Nov 28. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22123253 Free PMC article.
-
Biological roles of two new murein hydrolases of Streptococcus pneumoniae representing examples of module shuffling.Res Microbiol. 2000 Jul-Aug;151(6):437-43. doi: 10.1016/s0923-2508(00)00172-8. Res Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10961456 Review.
-
Bacterial peptidoglycan (murein) hydrolases.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008 Mar;32(2):259-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00099.x. Epub 2008 Feb 11. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18266855 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene Regulation by the LiaSR Two-Component System in Streptococcus mutans.PLoS One. 2015 May 28;10(5):e0128083. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128083. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26020679 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome analysis of a daptomycin-susceptible enterococcus faecium strain and its daptomycin-resistant variant arising during therapy.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Jan;57(1):261-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01454-12. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23114757 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational analyses of open reading frames within the vraSR operon and their roles in the cell wall stress response of Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Apr;55(4):1391-402. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01213-10. Epub 2011 Jan 10. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21220524 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of YthA, a PspC Family Transcriptional Regulator of Lactococcus lactis F44 Acid Tolerance and Nisin Yield: a Transcriptomic Approach.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Mar 1;84(6):e02483-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02483-17. Print 2018 Mar 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29305506 Free PMC article.
-
A liaR deletion restores susceptibility to daptomycin and antimicrobial peptides in multidrug-resistant Enterococcus faecalis.J Infect Dis. 2015 Apr 15;211(8):1317-25. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu602. Epub 2014 Oct 31. J Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25362197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bateman, A., and N. D. Rawlings. 2003. The CHAP domain: a large family of amidases including GSP amidase and peptidoglycan hydrolases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 28:234-237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

