Tn502 and Tn512 are res site hunters that provide evidence of resolvase-independent transposition to random sites
- PMID: 20118251
- PMCID: PMC2838034
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01322-09
Tn502 and Tn512 are res site hunters that provide evidence of resolvase-independent transposition to random sites
Abstract
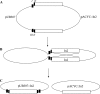
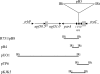
In this study, we report on the transposition behavior of the mercury(II) resistance transposons Tn502 and Tn512, which are members of the Tn5053 family. These transposons exhibit targeted and oriented insertion in the par region of plasmid RP1, since par-encoded components, namely, the ParA resolvase and its cognate res region, are essential for such transposition. Tn502 and, under some circumstances, Tn512 can transpose when par is absent, providing evidence for an alternative, par-independent pathway of transposition. We show that the alternative pathway proceeds by a two-step replicative process involving random target selection and orientation of insertion, leading to the formation of cointegrates as the predominant product of the first stage of transposition. Cointegrates remain unresolved because the transposon-encoded (TniR) recombination system is relatively inefficient, as is the host-encoded (RecA) system. In the presence of the res-ParA recombination system, TniR-mediated (and RecA-mediated) cointegrate resolution is highly efficient, enabling resolution both of cointegrates involving functional transposons (Tn502 and Tn512) and of defective elements (In0 and In2). These findings implicate the target-encoded accessory functions in the second stage of transposition as well as in the first. We also show that the par-independent pathway enables the formation of deletions in the target molecule.
Figures
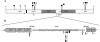

Similar articles
-
Mercury(II)-resistance transposons Tn502 and Tn512, from Pseudomonas clinical strains, are structurally different members of the Tn5053 family.Plasmid. 2011 Jan;65(1):58-64. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2010.08.003. Epub 2010 Aug 25. Plasmid. 2011. PMID: 20800080
-
Four genes, two ends, and a res region are involved in transposition of Tn5053: a paradigm for a novel family of transposons carrying either a mer operon or an integron.Mol Microbiol. 1995 Sep;17(6):1189-200. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.mmi_17061189.x. Mol Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 8594337
-
Tn5053 family transposons are res site hunters sensing plasmidal res sites occupied by cognate resolvases.Mol Microbiol. 1999 Sep;33(5):1059-68. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01548.x. Mol Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10476039
-
Structures bounded by directly-oriented members of the IS26 family are pseudo-compound transposons.Plasmid. 2020 Sep;111:102530. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2020.102530. Epub 2020 Aug 29. Plasmid. 2020. PMID: 32871211 Review.
-
Transposition in prokaryotes: transposon Tn501.Res Microbiol. 1991 Jul-Aug;142(6):689-700. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90082-l. Res Microbiol. 1991. PMID: 1660177 Review.
Cited by
-
Tn6249, a new Tn6162 transposon derivative carrying a double-integron platform and involved with acquisition of the blaVIM-1 metallo-β-lactamase gene in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Mar;59(3):1583-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04047-14. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25547348 Free PMC article.
-
Natural and Engineered Guide RNA-Directed Transposition with CRISPR-Associated Tn7-Like Transposons.Annu Rev Biochem. 2024 Aug;93(1):139-161. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-030122-041908. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Annu Rev Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38598855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Considerations for the Analysis of Bacterial Membrane Vesicles: Methods of Vesicle Production and Quantification Can Influence Biological and Experimental Outcomes.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0127321. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.01273-21. Epub 2021 Dec 22. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34937167 Free PMC article.
-
A programmable seekRNA guides target selection by IS1111 and IS110 type insertion sequences.Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 19;15(1):5235. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49474-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38898016 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics of 28 Salmonella enterica isolates: evidence for CRISPR-mediated adaptive sublineage evolution.J Bacteriol. 2011 Jul;193(14):3556-68. doi: 10.1128/JB.00297-11. Epub 2011 May 20. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21602358 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barkay, T., S. M. Miller, and A. O. Summers. 2003. Bacterial mercury resistance from atom to ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 27:355-384. - PubMed
-
- Bennett, P. M., J. Grinsted, and M. H. Richmond. 1977. Transposition of TnA does not generate deletions. Mol. Gen. Genet. 154:205-211. - PubMed
-
- Bolivar, F., R. L. Rodriguez, P. J. Green, M. C. Betlach, H. L. Heyneker, and H. W. Boyer. 1977. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene 2:95-113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

