Reclassification of the polyphyletic genus Prosthecomicrobium to form two novel genera, Vasilyevaea gen. nov. and Bauldia gen. nov. with four new combinations: Vasilyevaea enhydra comb. nov., Vasilyevaea mishustinii comb. nov., Bauldia consociata comb. nov. and Bauldia litoralis comb. nov
- PMID: 20118292
- PMCID: PMC3052453
- DOI: 10.1099/ijs.0.018234-0
Reclassification of the polyphyletic genus Prosthecomicrobium to form two novel genera, Vasilyevaea gen. nov. and Bauldia gen. nov. with four new combinations: Vasilyevaea enhydra comb. nov., Vasilyevaea mishustinii comb. nov., Bauldia consociata comb. nov. and Bauldia litoralis comb. nov
Abstract
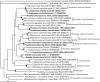
Species of the genus Prosthecomicrobium are noted for their numerous cellular appendages or prosthecae that extend from the cells. This investigation confirms that the genus is polyphyletic based on an extensive analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequences of several named species of the genus. The analyses indicate that some Prosthecomicrobium species are more closely related to non-prosthecate genera, including Devosia, Labrenzia, Blastochloris, Methylosinus, Mesorhizobium and Kaistia, than they are to other species of the genus Prosthecomicrobium. For this reason, two of the Prosthecomicrobium clades which are polyphyletic with the type species, Prosthecomicrobium pneumaticum, are renamed as new genera. The currently named species Prosthecomicrobium enhydrum, Prosthecomicrobium mishustinii, Prosthecomicrobium consociatum and Prosthecomicrobium litoralum are reclassified in two new genera, Vasilyevaea gen. nov. and Bauldia gen. nov. with four new combinations: Vasilyevaea enhydra comb. nov. (the type species) and Vasilyevaea mishustinii comb. nov., and Bauldia consociata comb. nov. and Bauldia litoralis comb. nov. (the type species). The type strain of Vasilyevaea enhydra is strain 9b(T) (=ATCC 23634(T) =VKM B-1376(T)). The type strain of the other species in this genus is Vasilyevaea mishustinii strain 17(T) (=VKM B-2499(T) =CCM 7569(T)). The type strain of Bauldia litoralis is strain 524-16(T) (= NCIB 2233(T) =ATCC 35022(T)). The type strain of the other species in this genus is Bauldia consociata strain 11(T) (=VKM B-2498(T) =CCM 7594(T)).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Devosia confluentis sp. nov., isolated from the junction between the ocean and a freshwater lake, and reclassification of two Vasilyevaea species as Devosia enhydra comb. nov. and Devosia mishustinii comb. nov.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2016 Oct;66(10):3935-3941. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001291. Epub 2016 Jul 8. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27393696
-
Description of Labrenzia alexandrii gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel alphaproteobacterium containing bacteriochlorophyll a, and a proposal for reclassification of Stappia aggregata as Labrenzia aggregata comb. nov., of Stappia marina as Labrenzia marina comb. nov. and of Stappia alba as Labrenzia alba comb. nov., and emended descriptions of the genera Pannonibacter, Stappia and Roseibium, and of the species Roseibium denhamense and Roseibium hamelinense.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2007 May;57(Pt 5):1095-1107. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.64821-0. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17473266
-
Phylogenetic analyses of the genus Glaciecola: emended description of the genus Glaciecola, transfer of Glaciecola mesophila, G. agarilytica, G. aquimarina, G. arctica, G. chathamensis, G. polaris and G. psychrophila to the genus Paraglaciecola gen. nov. as Paraglaciecola mesophila comb. nov., P. agarilytica comb. nov., P. aquimarina comb. nov., P. arctica comb. nov., P. chathamensis comb. nov., P. polaris comb. nov. and P. psychrophila comb. nov., and description of Paraglaciecola oceanifecundans sp. nov., isolated from the Southern Ocean.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2014 Sep;64(Pt 9):3264-3275. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.065409-0. Epub 2014 Jun 30. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24981324
-
Review of the genus Methylobacterium and closely related organisms: a proposal that some Methylobacterium species be reclassified into a new genus, Methylorubrum gen. nov.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2018 Sep;68(9):2727-2748. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.002856. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30024371 Review.
-
Tirons of the world: a review of tironid amphipods, description of new genera and species, and establishment of a new subfamily Tironinae Stebbing, 1906 stat. nov. (Crustacea, Synopiidae).Zootaxa. 2022 May 23;5139(1):1-89. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.5139.1.1. Zootaxa. 2022. PMID: 36095812 Review.
Cited by
-
Seasonal Dynamics of Sediment Microbial Communities at Different Distances from Artificial Reef Units.Microorganisms. 2025 May 23;13(6):1194. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13061194. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40572082 Free PMC article.
-
Nutrient availability and plant phenological stage influence the substrate microbiome in container-grown Impatiens walleriana 'Xtreme Red'.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Mar 6;24(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-04854-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38448825 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of 1,000+ Type-Strain Genomes Substantially Improves Taxonomic Classification of Alphaproteobacteria.Front Microbiol. 2020 Apr 7;11:468. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00468. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32373076 Free PMC article.
-
Polar growth in the Alphaproteobacterial order Rhizobiales.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jan 31;109(5):1697-701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1114476109. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22307633 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity Takes Shape: Understanding the Mechanistic and Adaptive Basis of Bacterial Morphology.PLoS Biol. 2016 Oct 3;14(10):e1002565. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002565. eCollection 2016 Oct. PLoS Biol. 2016. PMID: 27695035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bauld, J., Bigford, R. & Staley, J. T. (1983). Prosthecomicrobium litoralum, a new species from marine habitats. Int J Syst Bacteriol 33, 613–617.
-
- Cole, J. R., Chai, B., Marsh, T. L., Farris, R. J., Wang, Q., Kulam, S. A., Chandra, S., McGarrell, D. M., Schmidt, T. M. & other authors (2003). The Ribosomal Database Project (RDP-II): previewing a new autoaligner that allows regular updates and the new prokaryotic taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res 31, 442–443. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Felsenstein, J. (2007). phylip (phylogeny inference package) version 3.67. Distributed by the author. Department of Genome Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle, USA. http://evolution.genetics.washington.edu/phylip.html
-
- Hiraishi, A. (1997). Transfer of the bacteriochlorophyll b-containing phototrophic bacteria Rhodopseudomonas viridis and Rhodopseudomonas sulfoviridis to the genus Blastochloris gen. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47, 217–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

