Dual-source computed tomographic temporal resolution provides higher image quality than 64-detector temporal resolution at low heart rates
- PMID: 20118724
- PMCID: PMC2923656
- DOI: 10.1097/RCT.0b013e3181b67163
Dual-source computed tomographic temporal resolution provides higher image quality than 64-detector temporal resolution at low heart rates
Abstract
Objective: To compare coronary image quality at temporal resolutions associated with dual-source computed tomography (DSCT; 83 milliseconds) and 64-detector row scanning (165 milliseconds).
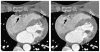
Methods: In 30 patients with a heart rate of less than 70 beats per minute, DSCT coronary angiograms were reconstructed at 83- and 165-millisecond temporal resolutions over different cardiac phases. A blinded observer graded coronary quality.
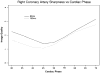
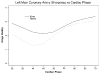
Results: The typical DSCT temporal resolution (83 milliseconds) showed a significantly greater quality at end-systole for all coronary vessels and at end-diastole for the right coronary and left anterior descending coronary arteries. For all vessels, the end-diastole produced the highest quality for both temporal resolutions.
Conclusions: Imaging at 83 milliseconds creates superior quality at end-systole for all coronary vessels and at end-diastole for the right coronary and left anterior descending coronary arteries. At low heart rates, end-diastole produces the highest quality at both temporal resolutions.
Figures
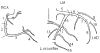



Similar articles
-
Optimal image reconstruction phase at low and high heart rates in dual-source CT coronary angiography.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2009 Dec;25(8):837-45. doi: 10.1007/s10554-009-9489-3. Epub 2009 Aug 9. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2009. PMID: 19669664 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-source CT coronary angiography in patients with atrial fibrillation: comparison with single-source CT.Eur J Radiol. 2008 Dec;68(3):434-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2008.09.011. Epub 2008 Nov 6. Eur J Radiol. 2008. PMID: 18993003
-
Noninvasive coronary angiography using dual-source computed tomography in patients with atrial fibrillation.Invest Radiol. 2009 Mar;44(3):159-67. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3181948b05. Invest Radiol. 2009. PMID: 19151607
-
Assessment of image quality of 64-row Dual Source versus Single Source CT coronary angiography on heart rate: a phantom study.Eur J Radiol. 2009 Apr;70(1):61-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2008.01.011. Epub 2008 Mar 4. Eur J Radiol. 2009. PMID: 18308496
-
Current and Novel Imaging Techniques in Coronary CT.Radiographics. 2015 Jul-Aug;35(4):991-1010. doi: 10.1148/rg.2015140181. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Radiographics. 2015. PMID: 26046942 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of multimodality imaging in ischemic and non-ischemic cardiomyopathy.Heart Fail Rev. 2011 Jul;16(4):351-67. doi: 10.1007/s10741-010-9218-y. Heart Fail Rev. 2011. PMID: 21165696 Review.
-
Radiation dose reduction in pediatric cardiac computed tomography: experience from a tertiary medical center.Pediatr Cardiol. 2014 Jan;35(1):171-9. doi: 10.1007/s00246-013-0758-5. Epub 2013 Jul 20. Pediatr Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 23872908
References
-
- Wintersperger BJ, Nikolaou K, von Ziegler F, et al. Image quality, motion artifacts, and reconstruction timing of 64-slice coronary computed tomography angiography with 0.33-second rotation speed. Invest Radiol. 2006;41:436–442. - PubMed
-
- Vanhoenacker PK, Heijenbrok-Kal MH, Van Heste R, et al. Diagnostic performance of multidetector CT angiography for assessment of coronary artery disease: meta-analysis. Radiology. 2007;244:419–428. - PubMed
-
- Flohr TG, McCollough CH, Bruder H, et al. First performance evaluation of a dual-source CT (DSCT) system. Eur Radiol. 2006;16:256–268. - PubMed
-
- Ropers U, Ropers D, Pflederer T, et al. Influence of heart rate on the diagnostic accuracy of dual-source computed tomography coronary angiography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50:2393–2398. - PubMed
-
- Heuschmid M, Burgstahler C, Reimann A, et al. Usefulness of noninvasive cardiac imaging using dual-source computed tomography in an unselected population with high prevalence of coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 2007;100:587–592. - PubMed

