Real-time imaging of hepatitis C virus infection using a fluorescent cell-based reporter system
- PMID: 20118917
- PMCID: PMC2828266
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.1604
Real-time imaging of hepatitis C virus infection using a fluorescent cell-based reporter system
Abstract
Hepatitis C virus (HCV), which infects 2-3% of the world population, is a causative agent of chronic hepatitis and the leading indication for liver transplantation. The ability to propagate HCV in cell culture (HCVcc) is a relatively recent breakthrough and a key tool in the quest for specific antiviral therapeutics. Monitoring HCV infection in culture generally involves bulk population assays, use of genetically modified viruses and/or terminal processing of potentially precious samples. Here we develop a cell-based fluorescent reporter system that allows sensitive distinction of individual HCV-infected cells in live or fixed samples. We demonstrate use of this technology for several previously intractable applications, including live-cell imaging of viral propagation and host response, as well as visualizing infection of primary hepatocyte cultures. Integration of this reporter with modern image-based analysis methods could open new doors for HCV research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
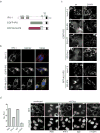
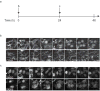
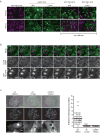
Comment in
-
Hepatitis C virus infection in living color.Hepatology. 2010 May;51(5):1852-5. doi: 10.1002/hep.23695. Hepatology. 2010. PMID: 20432262 No abstract available.
References
-
- Shepard CW, Finelli L, Alter MJ. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5:558–567. - PubMed
-
- Meylan E, et al. Cardif is an adaptor protein in the RIG-I antiviral pathway and is targeted by hepatitis C virus. Nature. 2005;437:1167–1172. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, et al. IPS-1, an adaptor triggering RIG-I- and Mda5-mediated type I interferon induction. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:981–988. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

