A map of open chromatin in human pancreatic islets
- PMID: 20118932
- PMCID: PMC2828505
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.530
A map of open chromatin in human pancreatic islets
Abstract
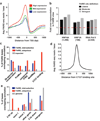
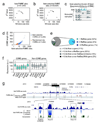
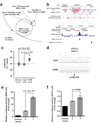
Tissue-specific transcriptional regulation is central to human disease. To identify regulatory DNA active in human pancreatic islets, we profiled chromatin by formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements coupled with high-throughput sequencing (FAIRE-seq). We identified approximately 80,000 open chromatin sites. Comparison of FAIRE-seq data from islets to that from five non-islet cell lines revealed approximately 3,300 physically linked clusters of islet-selective open chromatin sites, which typically encompassed single genes that have islet-specific expression. We mapped sequence variants to open chromatin sites and found that rs7903146, a TCF7L2 intronic variant strongly associated with type 2 diabetes, is located in islet-selective open chromatin. We found that human islet samples heterozygous for rs7903146 showed allelic imbalance in islet FAIRE signals and that the variant alters enhancer activity, indicating that genetic variation at this locus acts in cis with local chromatin and regulatory changes. These findings illuminate the tissue-specific organization of cis-regulatory elements and show that FAIRE-seq can guide the identification of regulatory variants underlying disease susceptibility.
Figures

Comment in
-
Open chromatin and diabetes risk.Nat Genet. 2010 Mar;42(3):190-2. doi: 10.1038/ng0310-190. Nat Genet. 2010. PMID: 20179731 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Mapping open chromatin with formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;791:287-96. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-316-5_21. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21913087
-
Pancreatic islet chromatin accessibility and conformation reveals distal enhancer networks of type 2 diabetes risk.Nat Commun. 2019 May 7;10(1):2078. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09975-4. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31064983 Free PMC article.
-
Open chromatin defined by DNaseI and FAIRE identifies regulatory elements that shape cell-type identity.Genome Res. 2011 Oct;21(10):1757-67. doi: 10.1101/gr.121541.111. Epub 2011 Jul 12. Genome Res. 2011. PMID: 21750106 Free PMC article.
-
Formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2009 Nov-Dec;1(3):400-406. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.36. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2009. PMID: 20046543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pancreatic Islet Transcriptional Enhancers and Diabetes.Curr Diab Rep. 2019 Nov 21;19(12):145. doi: 10.1007/s11892-019-1230-6. Curr Diab Rep. 2019. PMID: 31754873 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The selection and function of cell type-specific enhancers.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Mar;16(3):144-54. doi: 10.1038/nrm3949. Epub 2015 Feb 4. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25650801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Network Approaches for Dissecting the Immune System.iScience. 2020 Aug 21;23(8):101354. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101354. Epub 2020 Jul 10. iScience. 2020. PMID: 32717640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multidimensional chromatin profiling of zebrafish pancreas to uncover and investigate disease-relevant enhancers.Nat Commun. 2022 Apr 11;13(1):1945. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29551-7. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35410466 Free PMC article.
-
Galaxy: a comprehensive approach for supporting accessible, reproducible, and transparent computational research in the life sciences.Genome Biol. 2010;11(8):R86. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-8-r86. Epub 2010 Aug 25. Genome Biol. 2010. PMID: 20738864 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the effects of SNPs on transcription factor binding affinity.Bioinformatics. 2020 Jan 15;36(2):364-372. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz612. Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 31373606 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grant SF, et al. Variant of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene confers risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet. 2006;38:320–323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

