Homeostatic competition drives tumor growth and metastasis nucleation
- PMID: 20119483
- PMCID: PMC2799988
- DOI: 10.2976/1.3086732
Homeostatic competition drives tumor growth and metastasis nucleation
Abstract
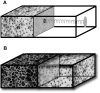
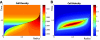
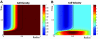
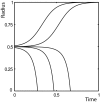
We propose a mechanism for tumor growth emphasizing the role of homeostatic regulation and tissue stability. We show that competition between surface and bulk effects leads to the existence of a critical size that must be overcome by metastases to reach macroscopic sizes. This property can qualitatively explain the observed size distributions of metastases, while size-independent growth rates cannot account for clinical and experimental data. In addition, it potentially explains the observed preferential growth of metastases on tissue surfaces and membranes such as the pleural and peritoneal layers, suggests a mechanism underlying the seed and soil hypothesis introduced by Stephen Paget in 1889, and yields realistic values for metastatic inefficiency. We propose a number of key experiments to test these concepts. The homeostatic pressure as introduced in this work could constitute a quantitative, experimentally accessible measure for the metastatic potential of early malignant growths.
Figures


References
-
- Cameron, M D, Schmidt, E E, Kerkvliet, N, Nadkarni, K V, Morris, V L, Groom, A C, Chambers, A F, and MacDonald, I C (2000). “Temporal progression of metastasis in lung: cell survival, dormancy, and location dependence of metastatic inefficiency: 1.” Cancer Res. CNREA8 60, 2541–2546. - PubMed
-
- Chambers, A F, and Wilson, S (1988). “Use of Neo R B16F1 murine melanoma cells to assess clonality of experimental metastases in the immune-deficient chick embryo.” Clin. Exp. Metastasis ZZZZZZ 6, 171–182. - PubMed
-
- Chaplain, M A. J, Graziano, L, and Preziosi, L (2006). “Mathematical modelling of the loss of tissue compression responsiveness and its role in solid tumour development.” Math. Med. Biol. 23, 197–229. - PubMed
-
- Couzin, J (2003). “Tracing the steps of metastasis, cancer’s menacing ballet.” Science SCIEAS 299, 1002–1006. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
